genomics
Immune Resilience is Key to a Long and Healthy Life
Posted on by Lawrence Tabak, D.D.S., Ph.D.

Do you feel as if you or perhaps your family members are constantly coming down with illnesses that drag on longer than they should? Or, maybe you’re one of those lucky people who rarely becomes ill and, if you do, recovers faster than others.
It’s clear that some people generally are more susceptible to infectious illnesses, while others manage to stay healthier or bounce back more quickly, sometimes even into old age. Why is this? A new study from an NIH-supported team has an intriguing answer [1]. The difference, they suggest, may be explained in part by a new measure of immunity they call immune resilience—the ability of the immune system to rapidly launch attacks that defend effectively against infectious invaders and respond appropriately to other types of inflammatory stressors, including aging or other health conditions, and then quickly recover, while keeping potentially damaging inflammation under wraps.
The findings in the journal Nature Communications come from an international team led by Sunil Ahuja, University of Texas Health Science Center and the Department of Veterans Affairs Center for Personalized Medicine, both in San Antonio. To understand the role of immune resilience and its effect on longevity and health outcomes, the researchers looked at multiple other studies including healthy individuals and those with a range of health conditions that challenged their immune systems.
By looking at multiple studies in varied infectious and other contexts, they hoped to find clues as to why some people remain healthier even in the face of varied inflammatory stressors, ranging from mild to more severe. But to understand how immune resilience influences health outcomes, they first needed a way to measure or grade this immune attribute.
The researchers developed two methods for measuring immune resilience. The first metric, a laboratory test called immune health grades (IHGs), is a four-tier grading system that calculates the balance between infection-fighting CD8+ and CD4+ T-cells. IHG-I denotes the best balance tracking the highest level of resilience, and IHG-IV denotes the worst balance tracking the lowest level of immune resilience. An imbalance between the levels of these T cell types is observed in many people as they age, when they get sick, and in people with autoimmune diseases and other conditions.
The researchers also developed a second metric that looks for two patterns of expression of a select set of genes. One pattern associated with survival and the other with death. The survival-associated pattern is primarily related to immune competence, or the immune system’s ability to function swiftly and restore activities that encourage disease resistance. The mortality-associated genes are closely related to inflammation, a process through which the immune system eliminates pathogens and begins the healing process but that also underlies many disease states.
Their studies have shown that high expression of the survival-associated genes and lower expression of mortality-associated genes indicate optimal immune resilience, correlating with a longer lifespan. The opposite pattern indicates poor resilience and a greater risk of premature death. When both sets of genes are either low or high at the same time, immune resilience and mortality risks are more moderate.
In the newly reported study initiated in 2014, Ahuja and his colleagues set out to assess immune resilience in a collection of about 48,500 people, with or without various acute, repetitive, or chronic challenges to their immune systems. In an earlier study, the researchers showed that this novel way to measure immune status and resilience predicted hospitalization and mortality during acute COVID-19 across a wide age spectrum [2].
The investigators have analyzed stored blood samples and publicly available data representing people, many of whom were healthy volunteers, who had enrolled in different studies conducted in Africa, Europe, and North America. Volunteers ranged in age from 9 to 103 years. They also evaluated participants in the Framingham Heart Study, a long-term effort to identify common factors and characteristics that contribute to cardiovascular disease.
To examine people with a wide range of health challenges and associated stresses on their immune systems, the team also included participants who had influenza or COVID-19, and people living with HIV. They also included kidney transplant recipients, people with lifestyle factors that put them at high risk for sexually transmitted infections, and people who’d had sepsis, a condition in which the body has an extreme and life-threatening response following an infection.
The question in all these contexts was the same: How well did the two metrics of immune resilience predict an individual’s health outcomes and lifespan? The short answer is that immune resilience, longevity, and better health outcomes tracked together well. Those with metrics indicating optimal immune resilience generally had better health outcomes and lived longer than those who had lower scores on the immunity grading scale. Indeed, those with optimal immune resilience were more likely to:
- Live longer,
- Resist HIV infection or the progression from HIV to AIDS,
- Resist symptomatic influenza,
- Resist a recurrence of skin cancer after a kidney transplant,
- Survive COVID-19, and
- Survive sepsis.
The study also revealed other interesting findings. While immune resilience generally declines with age, some people maintain higher levels of immune resilience as they get older for reasons that aren’t yet known, according to the researchers. Some people also maintain higher levels of immune resilience despite the presence of inflammatory stress to their immune systems such as during HIV infection or acute COVID-19. People of all ages can show high or low immune resilience. The study also found that higher immune resilience is more common in females than it is in males.
The findings suggest that there is a lot more to learn about why people differ in their ability to preserve optimal immune resilience. With further research, it may be possible to develop treatments or other methods to encourage or restore immune resilience as a way of improving general health, according to the study team.
The researchers suggest it’s possible that one day checkups of a person’s immune resilience could help us to understand and predict an individual’s health status and risk for a wide range of health conditions. It could also help to identify those individuals who may be at a higher risk of poor outcomes when they do get sick and may need more aggressive treatment. Researchers may also consider immune resilience when designing vaccine clinical trials.
A more thorough understanding of immune resilience and discovery of ways to improve it may help to address important health disparities linked to differences in race, ethnicity, geography, and other factors. We know that healthy eating, exercising, and taking precautions to avoid getting sick foster good health and longevity; in the future, perhaps we’ll also consider how our immune resilience measures up and take steps to achieve or maintain a healthier, more balanced, immunity status.
References:
[1] Immune resilience despite inflammatory stress promotes longevity and favorable health outcomes including resistance to infection. Ahuja SK, Manoharan MS, Lee GC, McKinnon LR, Meunier JA, Steri M, Harper N, Fiorillo E, Smith AM, Restrepo MI, Branum AP, Bottomley MJ, Orrù V, Jimenez F, Carrillo A, Pandranki L, Winter CA, Winter LA, Gaitan AA, Moreira AG, Walter EA, Silvestri G, King CL, Zheng YT, Zheng HY, Kimani J, Blake Ball T, Plummer FA, Fowke KR, Harden PN, Wood KJ, Ferris MT, Lund JM, Heise MT, Garrett N, Canady KR, Abdool Karim SS, Little SJ, Gianella S, Smith DM, Letendre S, Richman DD, Cucca F, Trinh H, Sanchez-Reilly S, Hecht JM, Cadena Zuluaga JA, Anzueto A, Pugh JA; South Texas Veterans Health Care System COVID-19 team; Agan BK, Root-Bernstein R, Clark RA, Okulicz JF, He W. Nat Commun. 2023 Jun 13;14(1):3286. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-38238-6. PMID: 37311745.
[2] Immunologic resilience and COVID-19 survival advantage. Lee GC, Restrepo MI, Harper N, Manoharan MS, Smith AM, Meunier JA, Sanchez-Reilly S, Ehsan A, Branum AP, Winter C, Winter L, Jimenez F, Pandranki L, Carrillo A, Perez GL, Anzueto A, Trinh H, Lee M, Hecht JM, Martinez-Vargas C, Sehgal RT, Cadena J, Walter EA, Oakman K, Benavides R, Pugh JA; South Texas Veterans Health Care System COVID-19 Team; Letendre S, Steri M, Orrù V, Fiorillo E, Cucca F, Moreira AG, Zhang N, Leadbetter E, Agan BK, Richman DD, He W, Clark RA, Okulicz JF, Ahuja SK. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2021 Nov;148(5):1176-1191. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2021.08.021. Epub 2021 Sep 8. PMID: 34508765; PMCID: PMC8425719.
Links:
COVID-19 Research (NIH)
HIV Info (NIH)
Sepsis (National Institute of General Medical Sciences/NIH)
Sunil Ahuja (University of Texas Health Science Center, San Antonio)
Framingham Heart Study (National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute/NIH)
“A Secret to Health and Long Life? Immune Resilience, NIAID Grantees Report,” NIAID Now Blog, June 13, 2023
NIH Support: National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases; National Institute on Aging; National Institute of Mental Health; National Institute of General Medical Sciences; National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute
Case Study Unlocks Clues to Rare Resilience to Alzheimer’s Disease
Posted on by Lawrence Tabak, D.D.S., Ph.D.

Biomedical breakthroughs most often involve slow and steady research in studies involving large numbers of people. But sometimes careful study of even just one truly remarkable person can lead the way to fascinating discoveries with far-reaching implications.
An NIH-funded case study published recently in the journal Nature Medicine falls into this far-reaching category [1]. The report highlights the world’s second person known to have an extreme resilience to a rare genetic form of early onset Alzheimer’s disease. These latest findings in a single man follow a 2019 report of a woman with similar resilience to developing symptoms of Alzheimer’s despite having the same strong genetic predisposition for the disease [2].
The new findings raise important new ideas about the series of steps that may lead to Alzheimer’s and its dementia. They’re also pointing the way to key parts of the brain for cognitive resilience—and potentially new treatment targets—that may one day help to delay or even stop progression of Alzheimer’s.
The man in question is a member of a well-studied extended family from the country of Colombia. This group of related individuals, or kindred, is the largest in the world with a genetic variant called the “Paisa” mutation (or Presenilin-1 E280A). This Paisa variant follows an autosomal dominant pattern of inheritance, meaning that those with a single altered copy of the rare variant passed down from one parent usually develop mild cognitive impairment around the age of 44. They typically advance to full-blown dementia around the age of 50 and rarely live past the age of 60. This contrasts with the most common form of Alzheimer’s, which usually begins after age 65.
The new findings come from a team led by Yakeel Quiroz, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston; Joseph Arboleda-Velasquez, Massachusetts Eye and Ear, Boston; Diego Sepulveda-Falla, University Medical Center Hamburg-Eppendorf, Hamburg, Germany; and Francisco Lopera, University of Antioquia, Medellín, Colombia. Lopera first identified this family more than 30 years ago and has been studying them ever since.
In the new case report, the researchers identified a Colombian man who’d been married with two children and retired from his job as a mechanic in his early 60s. Despite carrying the Paisa mutation, his first cognitive assessment at age 67 showed he was cognitively intact, having limited difficulties with verbal learning skills or language. It wasn’t until he turned 70 that he was diagnosed with mild cognitive impairment—more than 20 years later than the expected age for this family—showing some decline in short-term memory and verbal fluency.
At age 73, he enrolled in the Colombia-Boston biomarker research study (COLBOS). This study is a collaborative project between the University of Antioquia and Massachusetts General Hospital involving approximately 6,000 individuals from the Paisa kindred. About 1,500 of those in the study carry the mutation that sets them up for early Alzheimer’s. As a member of the COLBOS study, the man underwent thorough neuroimaging tests to look for amyloid plaques and tau tangles, both of which are hallmarks of Alzheimer’s.
While this man died at age 74 with Alzheimer’s, the big question is: how did he stave off dementia for so long despite his poor genetic odds? The COLBOS study earlier identified a woman with a similar resilience to Alzheimer’s, which they traced to two copies of a rare, protective genetic variant called Christchurch. This variant affects a gene called apolipoprotein E (APOE3), which is well known for its influence on Alzheimer’s risk. However, the man didn’t carry this same protective variant.
The researchers still thought they’d find an answer in his genome and kept looking. While they found several variants of possible interest, they zeroed in on a single gene variant that they’ve named Reelin-COLBOS. What helped them to narrow it down to this variant is the man also had a sister with the Paisa mutation who only progressed to advanced dementia at age 72. It turned out, in addition to the Paisa variant, the siblings also shared an altered copy of the newly discovered Reelin-COLBOS variant.
This Reelin-COLBOS gene is known to encode a protein that controls signals to chemically modify tau proteins, which form tangles that build up over time in the Alzheimer’s brain and have been linked to memory loss. Reelin is also functionally related to APOE, the gene that was altered in the woman with extreme Alzheimer’s protection. Reelin and APOE both interact with common protein receptors in neurons. Together, the findings add to evidence that signaling pathways influencing tau play an important role in Alzheimer’s pathology and protection.
The neuroimaging exams conducted when the man was age 73 have offered further intriguing clues. They showed that his brain had extensive amyloid plaques. He also had tau tangles in some parts of his brain. But one brain region, called the entorhinal cortex, was notable for having a very minimal amount of those hallmark tau tangles.
The entorhinal cortex is a hub for memory, navigation, and the perception of time. Its degeneration also leads to cognitive impairment and dementia. Studies of the newly identified Reelin-COLBOS variant in Alzheimer’s mouse models also help to confirm that the variant offers its protection by diminishing the pathological modifications of tau.
Overall, the findings in this one individual and his sister highlight the Reelin pathway and brain region as promising targets for future study and development of Alzheimer’s treatments. Quiroz and her colleagues report that they are actively exploring treatment approaches inspired by the Christchurch and Reelin-COLBOS discoveries.
Of course, there’s surely more to discover from continued study of these few individuals and others like them. Other as yet undescribed genetic and environmental factors are likely at play. But the current findings certainly offer some encouraging news for those at risk for Alzheimer’s disease—and a reminder of how much can be learned from careful study of remarkable individuals.
References:
[1] Resilience to autosomal dominant Alzheimer’s disease in a Reelin-COLBOS heterozygous man. Lopera F, Marino C, Chandrahas AS, O’Hare M, Reiman EM, Sepulveda-Falla D, Arboleda-Velasquez JF, Quiroz YT, et al. Nat Med. 2023 May;29(5):1243-1252.
[2] Resistance to autosomal dominant Alzheimer’s disease in an APOE3 Christchurch homozygote: a case report. Arboleda-Velasquez JF, Lopera F, O’Hare M, Delgado-Tirado S, Tariot PN, Johnson KA, Reiman EM, Quiroz YT et al. Nat Med. 2019 Nov;25(11):1680-1683.
Links:
Alzheimer’s Disease & Related Dementias (National Institute on Aging/NIH)
“NIH Support Spurs Alzheimer’s Research in Colombia,” Global Health Matters, January/February 2014, Fogarty International Center/NIS
“COLBOS Study Reveals Mysteries of Alzheimer’s Disease,” NIH Record, August 19, 2022.
Yakeel Quiroz (Massachusetts General Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Boston)
Joseph Arboleda-Velasquez (Massachusetts Eye and Ear, Harvard Medical School, Boston)
Diego Sepulveda-Falla Lab (University Medical Center Hamburg-Eppendorf, Hamburg, Germany)
Francisco Lopera (University of Antioquia, Medellín, Colombia)
NIH Support: National Institute on Aging; National Eye Institute; National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke; Office of the Director
All of Us Research Program Participants Fuel Both Scientific and Personal Discovery
Posted on by Josh Denny, M.D., M.S., All of Us Research Program

The NIH’s All of Us Research Program is a historic effort to create an unprecedented research resource that will speed biomedical breakthroughs, transform medicine and advance health equity. To create this resource, we are enrolling at least 1 million people who reflect the diversity of the United States.
At the program’s outset, we promised to make research a two-way street by returning health information to our participant partners. We are now delivering on that promise. We are returning personalized health-related DNA reports to participants who choose to receive them.
That includes me. I signed up to receive my “Medicine and Your DNA” and “Hereditary Disease Risk” reports along with nearly 200,000 other participant partners. I recently read my results, and they hit home, revealing an eye-opening connection between my personal and professional lives.
First, the professional. Before coming to All of Us, I was a practicing physician and researcher at Vanderbilt University, Nashville, TN, where I studied how a person’s genes might affect his or her response to medications. One of the drug-gene interactions that I found most interesting is related to clopidogrel, a drug commonly prescribed to keep arteries open after a major cardiovascular event, like a heart attack, stroke, or placement of a stent.
People with certain gene variations are not able to process this medication well, leaving them in a potentially risky situation. The patient and their health care provider may think the condition is being managed. But, since they can’t process the medication, the patient’s symptoms and risks are likely to increase.
The impact on patients has been seen in numerous studies, including one that I published with colleagues last year in the Journal of Stroke and Cerebrovascular Disease [1]. We found that stroke risk is three times higher in patients who were poor responders to clopidogrel and treated with the drug following a “mini-stroke”—also known as a transient ischemic attack. Other studies have shown that major cardiovascular events were 50 percent more common in individuals who were poor responders to clopidogrel [2]. Importantly, there are alternative therapies that work well for people with this genetic variant.
Now, the personal. Reading my health-related results, I learned that I carry some of these very same gene variations. So, if I ever needed a medicine to manage my risk of blood clots, clopidogrel would not likely work well for me.
Instead, should I ever need treatment, my provider and I could bypass this common first-line therapy and choose an alternate medicine. Getting the right treatment on the first try could cut my chances of a heart attack in half. The benefits of this knowledge don’t stop with me. By choosing to share my findings with family members who may have inherited the same genetic variations, they can discuss it with their health care teams.
Other program participants who choose to receive results will experience the same process of learning more about their health. Nearly all will get actionable information about how their body may process certain medications. A small percentage, 2 to 3 percent, may learn they’re at higher risk of developing several severe hereditary health conditions, such as certain preventable heart diseases and cancers. The program will provide a genetic counselor at no cost to all participants to discuss their results.
To enroll participants who reflect the country’s diverse population, All of Us partners with trusted community organizations around the country. Inclusion is vitally important in the field of genomics research, where available data have long originated mostly from people of European ancestry. In contrast, about 50 percent of the All of Us’ genomic data come from individuals who self-identify with a racial or ethnic minority group.
More than 3,600 research projects are already underway using data contributed by participants from diverse backgrounds. What’s especially exciting about this “ecosystem” of discovery between participants and researchers is that, by contributing their data, participants are helping researchers decode what our DNA is telling us about health across all types of conditions. In turn, those discoveries will deepen what participants can learn.
Those who have stepped up to join All of Us are the heartbeat of this historic research effort to advance personalized approaches in medicine. Their contributions are already fueling new discoveries in numerous areas of health.
At the same time, making good on our promises to our participant partners ensures that the knowledge gained doesn’t only accumulate in a database but is delivered back to participants to help advance their own health journeys. If you’re interested in joining All of Us, we welcome you to learn more.
References:
[1] CYP2C19 loss-of-function is associated with increased risk of ischemic stroke after transient ischemic attack in intracranial atherosclerotic disease. Patel PD, Vimalathas P, Niu X, Shannon CN, Denny JC, Peterson JF, Chitale RV, Fusco MR. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2021 Feb;30(2):105464.
[2] Predicting clopidogrel response using DNA samples linked to an electronic health record. Delaney JT, Ramirez AH, Bowton E, Pulley JM, Basford MA, Schildcrout JS, Shi Y, Zink R, Oetjens M, Xu H, Cleator JH, Jahangir E, Ritchie MD, Masys DR, Roden DM, Crawford DC, Denny JC. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2012 Feb;91(2):257-263.
Links:
Join All of Us (All of Us/NIH)
NIH’s All of Us Research Program returns genetic health-related results to participants, NIH News Release, December 13, 2022.
NIH’s All of Us Research Program Releases First Genomic Dataset of Nearly 100,000 Whole Genome Sequences, NIH News Release, March 17, 2022.
Funding and Program Partners (All of Us)
Medicine and Your DNA (All of Us)
Clopidogrel Response (National Library of Medicine/NIH)
Hereditary Disease Risk (All of Us)
Preparing for DNA Results: What Is a Genetic Counselor? (All of Us)
Research Projects Directory (All of Us)
Note: Dr. Lawrence Tabak, who performs the duties of the NIH Director, has asked the heads of NIH’s Institutes, Centers, and Offices to contribute occasional guest posts to the blog to highlight some of the interesting science that they support and conduct. This is the 24th in the series of NIH guest posts that will run until a new permanent NIH director is in place.
A More Precise Way to Knock Out Skin Rashes
Posted on by Lawrence Tabak, D.D.S., Ph.D.
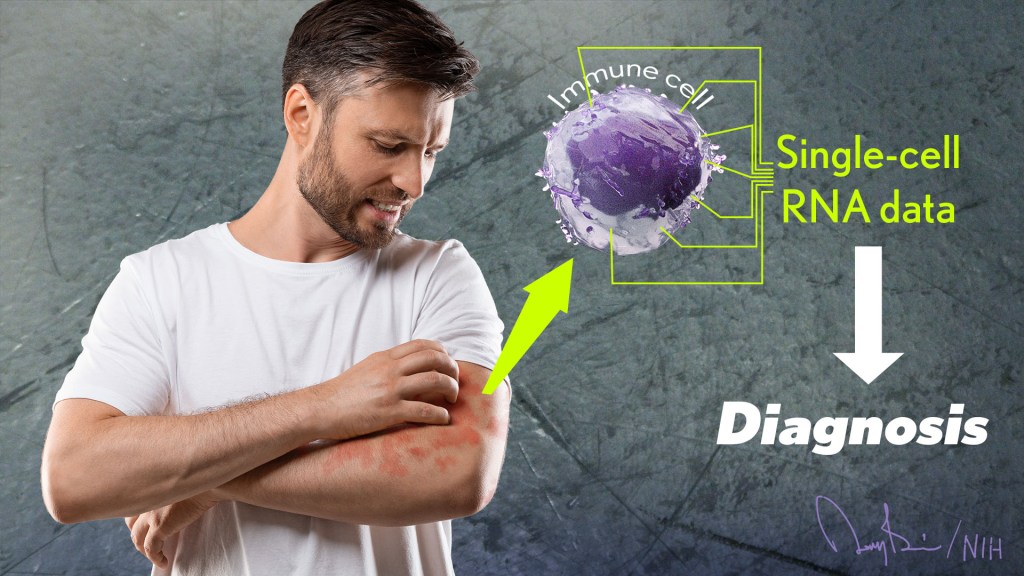
The NIH is committed to building a new era in medicine in which the delivery of health care is tailored specifically to the individual person, not the hypothetical average patient as is now often the case. This new era of “precision medicine” will transform care for many life-threatening diseases, including cancer and chronic kidney disease. But what about non-life-threatening conditions, like the aggravating rash on your skin that just won’t go away?
Recently, researchers published a proof-of-principle paper in the journal Science Immunology demonstrating just how precision medicine for inflammatory skin rashes might work [1]. While more research is needed to build out and further refine the approach, the researchers show it’s now technologically possible to extract immune cells from a patient’s rash, read each cell’s exact inflammatory features, and relatively quickly match them online to the right anti-inflammatory treatment to stop the rash.
The work comes from a NIH-funded team led by Jeffrey Cheng and Raymond Cho, University of California, San Francisco. The researchers focused their attention on two inflammatory skin conditions: atopic dermatitis, the most common type of eczema, which flares up periodically to make skin red and itchy, and psoriasis vulgaris. Psoriasis causes skin cells to build up and form a scaly rash and dry, itchy patches. Together, atopic dermatitis and psoriasis vulgaris affect about 10 percent of U.S. adults.
While the rashes caused by the two conditions can sometimes look similar, they are driven by different sets of immune cells and underlying inflammatory responses. For that reason, distinct biologic therapies, based on antibodies and proteins made from living cells, are now available to target and modify the specific immune pathways underlying each condition.
While biologic therapies represent a major treatment advance for these and other inflammatory conditions, they can miss their targets. Indeed, up to half of patients don’t improve substantially on biologics. Part of the reason for that lack of improvement is because doctors don’t have the tools they need to make firm diagnoses based on what precisely is going on in the skin at the molecular and cellular levels.
To learn more in the new study, the researchers isolated immune cells, focusing primarily on T cells, from the skin of 31 volunteers. They then sequenced the RNA of each cell to provide a telltale portrait of its genomic features. This “single-cell analysis” allowed them to capture high-resolution portraits of 41 different immune cell types found in individual skin samples. That’s important because it offers a much more detailed understanding of changes in the behavior of various immune cells that might have been missed in studies focused on larger groupings of skin cells, representing mixtures of various cell types.
Of the 31 volunteers, seven had atopic dermatitis and eight had psoriasis vulgaris. Three others were diagnosed with other skin conditions, while six had an indeterminate rash with features of both atopic dermatitis and psoriasis vulgaris. Seven others were healthy controls.
The team produced molecular signatures of the immune cells. The researchers then compared the signatures from the hard-to-diagnose rashes to those of confirmed cases of atopic dermatitis and psoriasis. They wanted to see if the signatures could help to reach clearer diagnoses.
The signatures revealed common immunological features as well as underlying differences. Importantly, the researchers found that the signatures allowed them to move forward and classify the indeterminate rashes. The rashes also responded to biologic therapies corresponding to the individuals’ new diagnoses.
Already, the work has identified molecules that help to define major classes of human inflammatory skin diseases. The team has also developed computer tools to help classify rashes in many other cases where the diagnosis is otherwise uncertain.
In fact, the researchers have launched a pioneering website called RashX. It is enabling practicing dermatologists and researchers around the world to submit their single-cell RNA data from their difficult cases. Such analyses are now being done at a small, but growing, number of academic medical centers.
While precision medicine for skin rashes has a long way to go yet before reaching most clinics, the UCSF team is working diligently to ensure its arrival as soon as scientifically possible. Indeed, their new data represent the beginnings of an openly available inflammatory skin disease resource. They ultimately hope to generate a standardized framework to link molecular features to disease prognosis and drug response based on data collected from clinical centers worldwide. It’s a major effort, but one that promises to improve the diagnosis and treatment of many more unusual and long-lasting rashes, both now and into the future.
Reference:
[1] Classification of human chronic inflammatory skin disease based on single-cell immune profiling. Liu Y, Wang H, Taylor M, Cook C, Martínez-Berdeja A, North JP, Harirchian P, Hailer AA, Zhao Z, Ghadially R, Ricardo-Gonzalez RR, Grekin RC, Mauro TM, Kim E, Choi J, Purdom E, Cho RJ, Cheng JB. Sci Immunol. 2022 Apr 15;7(70):eabl9165. {Epub ahead of publication]
Links:
The Promise of Precision Medicine (NIH)
Atopic Dermatitis (National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases /NIH)
Psoriasis (NIAMS/NIH)
RashX (University of California, San Francisco)
Raymond Cho (UCSF)
Jeffrey Cheng (UCSF)
NIH Support: National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases; National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences
All of Us: Release of Nearly 100,000 Whole Genome Sequences Sets Stage for New Discoveries
Posted on by Joshua Denny, M.D., M.S., and Lawrence Tabak, D.D.S., Ph.D.

Nearly four years ago, NIH opened national enrollment for the All of Us Research Program. This historic program is building a vital research community within the United States of at least 1 million participant partners from all backgrounds. Its unifying goal is to advance precision medicine, an emerging form of health care tailored specifically to the individual, not the average patient as is now often the case. As part of this historic effort, many participants have offered DNA samples for whole genome sequencing, which provides information about almost all of an individual’s genetic makeup.
Earlier this month, the All of Us Research Program hit an important milestone. We released the first set of nearly 100,000 whole genome sequences from our participant partners. The sequences are stored in the All of Us Researcher Workbench, a powerful, cloud-based analytics platform that makes these data broadly accessible to registered researchers.
The All of Us Research Program and its many participant partners are leading the way toward more equitable representation in medical research. About half of this new genomic information comes from people who self-identify with a racial or ethnic minority group. That’s extremely important because, until now, over 90 percent of participants in large genomic studies were of European descent. This lack of diversity has had huge impacts—deepening health disparities and hindering scientific discovery from fully benefiting everyone.
The Researcher Workbench also contains information from many of the participants’ electronic health records, Fitbit devices, and survey responses. Another neat feature is that the platform links to data from the U.S. Census Bureau’s American Community Survey to provide more details about the communities where participants live.
This unique and comprehensive combination of data will be key in transforming our understanding of health and disease. For example, given the vast amount of data and diversity in the Researcher Workbench, new diseases are undoubtedly waiting to be uncovered and defined. Many new genetic variants are also waiting to be identified that may better predict disease risk and response to treatment.
To speed up the discovery process, these data are being made available, both widely and wisely. To protect participants’ privacy, the program has removed all direct identifiers from the data and upholds strict requirements for researchers seeking access. Already, more than 1,500 scientists across the United States have gained access to the Researcher Workbench through their institutions after completing training and agreeing to the program’s strict rules for responsible use. Some of these researchers are already making discoveries that promote precision medicine, such as finding ways to predict how to best to prevent vision loss in patients with glaucoma.
Beyond making genomic data available for research, All of Us participants have the opportunity to receive their personal DNA results, at no cost to them. So far, the program has offered genetic ancestry and trait results to more than 100,000 participants. Plans are underway to begin sharing health-related DNA results on hereditary disease risk and medication-gene interactions later this year.
This first release of genomic data is a huge milestone for the program and for health research more broadly, but it’s also just the start. The program’s genome centers continue to generate the genomic data and process about 5,000 additional participant DNA samples every week.
The ultimate goal is to gather health data from at least 1 million or more people living in the United States, and there’s plenty of time to join the effort. Whether you would like to contribute your own DNA and health information, engage in research, or support the All of Us Research Program as a partner, it’s easy to get involved. By taking part in this historic program, you can help to build a better and more equitable future for health research and precision medicine.
Note: Joshua Denny, M.D., M.S., is the Chief Executive Officer of NIH’s All of Us Research Program.
Links:
All of Us Research Program (NIH)
Join All of Us (NIH)
Seeking Consensus on the Use of Population Descriptors in Genomics
Posted on by Eric Green, M.D., Ph.D., National Human Genome Research Institute
Cataloging and characterizing the thousands of genomic variants—differences in DNA sequences among individuals—across human populations is a foundational component of genomics. Scientists from various disciplinary fields compare the variation that occurs within and between the genomes of individuals and groups. Such efforts include attributing descriptors to population groups, which have historically included the use of social constructs such as race, ethnicity, ancestry, and political geographic location. Like any descriptors, these words do not fully account for the scope and diversity of the human species.
The use of race, ethnicity, and ancestry as descriptors of population groups in biomedical and genomics research has been a topic of consistent and rigorous debate within the scientific community. Human health, disease, and ancestry are all tied to how we define and explain human diversity. For centuries, scientists have incorrectly inferred that people of different races reflect discrete biological groups, which has led to deep-rooted health inequities and reinforced scientific racism.
In recent decades, genomics research has revealed the complexity of human genomic variation and the limitations of these socially derived population descriptors. The scientific community has long worked to move beyond the use of the social construct of race as a population descriptor and provide guidance about agreed-upon descriptors of human populations. Such a need has escalated with the growing numbers of large population-scale genomics studies being launched around the world, including in the United States.
To answer this call, NIH is sponsoring a National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine (NASEM) study that aims to develop best practices in the use of race, ethnicity, and genetic ancestry in genomics research. The NASEM study is sponsored by 14 NIH institutes, centers, offices, and programs, and the resulting report will be released in February 2023.
Experts from various fields—including genomics, medicine, and social sciences—are conducting the study. Much of the effort will revolve around reviewing and assessing existing methodologies, benefits, and challenges in the use of race and ethnicity and other population descriptors in genomics research. The ad hoc committee will host three public meetings to obtain input. Look for more information regarding the committee’s next public session planned for April 2022 on the NASEM “Race, Ethnicity, and Ancestry as Population Descriptors in Genomics Research” website.
To further underscore the need for the NASEM study, an NIH study published in December 2021 revealed that the descriptors for human populations used in the genetics literature have evolved over the last 70 years [1]. For example, the use of the word “race” has substantially decreased, while the uses of “ancestry” and “ethnicity” have increased. The study provided additional evidence that population descriptors often reflect fluid, social constructs whose intention is to describe groups with common genetic ancestry. These findings reinforce the timeliness of the NASEM study, with the clear need for experts to provide guidance for establishing more stable and meaningful population descriptors for use in future genomics studies.
The full promise of genomics, including its application to medicine, depends on improving how we explain human genomic variation. The words that we use to describe participants in research studies and populations must be transparent, thoughtful, and consistent—in addition to avoiding the perpetuation of structural racism. The best and most fruitful genomics research demands a better approach.
Reference:
[1] Evolving use of ancestry, ethnicity, and race in genetics research—A survey spanning seven decades. Byeon YJJ, Islamaj R, Yeganova L, Wilbur WJ, Lu Z, Brody LC, Bonham VL. Am J Hum Genet. 2021 Dec 2;108(12):2215-2223.
Links:
Use of Race, Ethnicity, and Ancestry as Population Descriptors in Genomics Research (National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine)
“Language used by researchers to describe human populations has evolved over the last 70 years.” (National Human Genome Research Institute/NIH)
Genomic Variation Program (NHGRI)
[Note: Acting NIH Director Lawrence Tabak has asked the heads of NIH’s institutes and centers to contribute occasional guest posts to the blog as a way to highlight some of the cool science that they support and conduct. This is the third in the series of NIH institute and center guest posts that will run until a new permanent NIH director is in place.]
New Technology Opens Evolutionary Window into Brain Development
Posted on by Dr. Francis Collins

One of the great mysteries in biology is how we humans ended up with such large, complex brains. In search of clues, researchers have spent years studying the protein-coding genes activated during neurodevelopment. But some answers may also be hiding in non-coding regions of the human genome, where sequences called regulatory elements increase or decrease the activity of genes.
A fascinating example involves a type of regulatory element called a human accelerated region (HAR). Although “human” is part of this element’s name, it turns out that the genomes of all vertebrates—not just humans—contain the DNA segments now designated as HARs.
In most organisms, HARs show a relatively low rate of mutation, which means these regulatory elements have been highly conserved across species throughout evolutionary time [1]. The big exception is Homo sapiens, in which HARs have exhibited a much higher rate of mutations.
The accelerated rate of HARs mutations observed in humans suggest that, over the course of very long periods of time, these genomic changes might have provided our species with some sort of evolutionary advantage. What might that be? Many have speculated the advantage might involve the brain because HARs are often associated with genes involved in neurodevelopment. Now, in a paper published in the journal Neuron, an NIH-supported team confirms that’s indeed the case [2].
In the new work, researchers found that about half of the HARs in the human genome influence the activity, or expression, of protein-coding genes in neural cells and tissues during the brain’s development [3]. The researchers say their study—the most comprehensive to date of the 3,171 HARs in the human genome—firmly establishes that this type of regulatory element helps to drive patterns of neurodevelopmental gene activity specific to humans.
Yet to be determined is precisely how HARs affect the development of the human brain. The quest to uncover these details will no doubt shed new light on fundamental questions about the brain, its billions of neurons, and their trillions of interconnections. For example, why does human neural development span decades, longer than the life spans of most primates and other mammals? Answering such questions could also reveal new clues into a range of cognitive and behavioral disorders. In fact, early research has already made tentative links between HARs and neurodevelopmental conditions such as autism spectrum disorder and schizophrenia [3].
The latest work was led by Kelly Girskis, Andrew Stergachis, and Ellen DeGennaro, all of whom were in the lab of Christopher Walsh while working on the project. An NIH grantee, Walsh is director of the Allen Discovery Center for Brain Evolution at Boston Children’s Hospital and Harvard Medical School, which is supported by the Paul G. Allen Foundation Frontiers Group, and is an Investigator of the Howard Hughes Medical Institute.
Though HARs have been studied since 2006, one of the big challenges in systematically assessing them has been technological. The average length of a HAR is about 269 bases of DNA, but current technologies for assessing function can only easily analyze DNA molecules that span 150 bases or less.
Ryan Doan, who was then in the Walsh Lab, and his colleagues solved the problem by creating a new machine called CaptureMPRA. (MPRA is short for “massively parallel reporter assays.”) This technological advance cleverly barcodes HARs and, more importantly, makes it possible to analyze HARs up to about 500 bases in length.
Using CaptureMPRA technology in tandem with cell culture studies, researchers rolled up their sleeves and conducted comprehensive, full-sequence analyses of more than 3,000 HARs. In their initial studies, primarily in neural cells, they found nearly half of human HARs are active to drive gene expression in cell culture. Of those, 42 percent proved to have increased ability to enhance gene expression compared to their orthologues, or counterparts, in chimpanzees.
Next, the team integrated these data with an existing epigenetic dataset derived from developing human brain cells, as well as additional datasets generated from sorted brain cell types. They found that many HARs appeared to have the ability to increase the activity of protein-coding genes, while a smaller—but very significant—subset of the HARs appeared to be enhancing gene expression specifically in neural progenitor cells, which are responsible for making various neural cell types.
The data suggest that as the human HAR sequences mutated and diverged from other mammals, they increased their ability to enhance or sometimes suppress the activity of certain genes in neural cells. To illustrate this point, the researchers focused on two HARs that appear to interact specifically with a gene referred to as R17. This gene can have highly variable gene expression patterns not only in different human cell types, but also in cells from other vertebrates and non-vertebrates.
In the human cerebral cortex, the outermost part of the brain that’s responsible for complex behaviors, R17 is expressed only in neural progenitor cells and only at specific time points. The researchers found that R17 slows the progression of neural progenitor cells through the cell cycle. That might seem strange, given the billions of neurons that need to be made in the cortex. But it’s consistent with the biology. In the human, it takes more than 130 days for the cortex to complete development, compared to about seven days in the mouse.
Clearly, to learn more about how the human brain evolved, researchers will need to look for clues in many parts of the genome at once, including its non-coding regions. To help researchers navigate this challenging terrain, the Walsh team has created an online resource displaying their comprehensive HAR data. It will appear soon, under the name HAR Hub, on the University of California Santa Cruz Genome Browser.
References:
[1] An RNA gene expressed during cortical development evolved rapidly in humans. Pollard KS, Salama SR, Lambert N, Lambot MA, Coppens S, Pedersen JS, Katzman S, King B, Onodera C, Siepel A, Kern AD, Dehay C, Igel H, Ares M Jr, Vanderhaeghen P, Haussler D. Nature. 2006 Sep 14;443(7108):167-72.
[2] Rewiring of human neurodevelopmental gene regulatory programs by human accelerated regions. Girskis KM, Stergachis AB, DeGennaro EM, Doan RN, Qian X, Johnson MB, Wang PP, Sejourne GM, Nagy MA, Pollina EA, Sousa AMM, Shin T, Kenny CJ, Scotellaro JL, Debo BM, Gonzalez DM, Rento LM, Yeh RC, Song JHT, Beaudin M, Fan J, Kharchenko PV, Sestan N, Greenberg ME, Walsh CA. Neuron. 2021 Aug 25:S0896-6273(21)00580-8.
[3] Mutations in human accelerated regions disrupt cognition and social behavior. Doan RN, Bae BI, Cubelos B, Chang C, Hossain AA, Al-Saad S, Mukaddes NM, Oner O, Al-Saffar M, Balkhy S, Gascon GG; Homozygosity Mapping Consortium for Autism, Nieto M, Walsh CA. Cell. 2016 Oct 6;167(2):341-354.
Links:
Christopher Walsh Laboratory (Boston Children’s Hospital and Harvard Medical School)
The Paul G. Allen Foundation Frontiers Group (Seattle)
NIH Support: National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke; National Institute of Mental Health; National Institute of General Medical Sciences; National Cancer Institute
Engineering a Better Way to Deliver Therapeutic Genes to Muscles
Posted on by Dr. Francis Collins

Amid all the progress toward ending the COVID-19 pandemic, it’s worth remembering that researchers here and around the world continue to make important advances in tackling many other serious health conditions. As an inspiring NIH-supported example, I’d like to share an advance on the use of gene therapy for treating genetic diseases that progressively degenerate muscle, such as Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD).
As published recently in the journal Cell, researchers have developed a promising approach to deliver therapeutic genes and gene editing tools to muscle more efficiently, thus requiring lower doses [1]. In animal studies, the new approach has targeted muscle far more effectively than existing strategies. It offers an exciting way forward to reduce unwanted side effects from off-target delivery, which has hampered the development of gene therapy for many conditions.
In boys born with DMD (it’s an X-linked disease and therefore affects males), skeletal and heart muscles progressively weaken due to mutations in a gene encoding a critical muscle protein called dystrophin. By age 10, most boys require a wheelchair. Sadly, their life expectancy remains less than 30 years.
The hope is gene therapies will one day treat or even cure DMD and allow people with the disease to live longer, high-quality lives. Unfortunately, the benign adeno-associated viruses (AAVs) traditionally used to deliver the healthy intact dystrophin gene into cells mostly end up in the liver—not in muscles. It’s also the case for gene therapy of many other muscle-wasting genetic diseases.
The heavy dose of viral vector to the liver is not without concern. Recently and tragically, there have been deaths in a high-dose AAV gene therapy trial for X-linked myotubular myopathy (XLMTM), a different disorder of skeletal muscle in which there may already be underlying liver disease, potentially increasing susceptibility to toxicity.
To correct this concerning routing error, researchers led by Mohammadsharif Tabebordbar in the lab of Pardis Sabeti, Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard and Harvard University, Cambridge, MA, have now assembled an optimized collection of AAVs. They have been refined to be about 10 times better at reaching muscle fibers than those now used in laboratory studies and clinical trials. In fact, researchers call them myotube AAVs, or MyoAAVs.
MyoAAVs can deliver therapeutic genes to muscle at much lower doses—up to 250 times lower than what’s needed with traditional AAVs. While this approach hasn’t yet been tried in people, animal studies show that MyoAAVs also largely avoid the liver, raising the prospect for more effective gene therapies without the risk of liver damage and other serious side effects.
In the Cell paper, the researchers demonstrate how they generated MyoAAVs, starting out with the commonly used AAV9. Their goal was to modify the outer protein shell, or capsid, to create an AAV that would be much better at specifically targeting muscle. To do so, they turned to their capsid engineering platform known as, appropriately enough, DELIVER. It’s short for Directed Evolution of AAV capsids Leveraging In Vivo Expression of transgene RNA.
Here’s how DELIVER works. The researchers generate millions of different AAV capsids by adding random strings of amino acids to the portion of the AAV9 capsid that binds to cells. They inject those modified AAVs into mice and then sequence the RNA from cells in muscle tissue throughout the body. The researchers want to identify AAVs that not only enter muscle cells but that also successfully deliver therapeutic genes into the nucleus to compensate for the damaged version of the gene.
This search delivered not just one AAV—it produced several related ones, all bearing a unique surface structure that enabled them specifically to target muscle cells. Then, in collaboration with Amy Wagers, Harvard University, Cambridge, MA, the team tested their MyoAAV toolset in animal studies.
The first cargo, however, wasn’t a gene. It was the gene-editing system CRISPR-Cas9. The team found the MyoAAVs correctly delivered the gene-editing system to muscle cells and also repaired dysfunctional copies of the dystrophin gene better than the CRISPR cargo carried by conventional AAVs. Importantly, the muscles of MyoAAV-treated animals also showed greater strength and function.
Next, the researchers teamed up with Alan Beggs, Boston Children’s Hospital, and found that MyoAAV was effective in treating mouse models of XLMTM. This is the very condition mentioned above, in which very high dose gene therapy with a current AAV vector has led to tragic outcomes. XLMTM mice normally die in 10 weeks. But, after receiving MyoAAV carrying a corrective gene, all six mice had a normal lifespan. By comparison, mice treated in the same way with traditional AAV lived only up to 21 weeks of age. What’s more, the researchers used MyoAAV at a dose 100 times lower than that currently used in clinical trials.
While further study is needed before this approach can be tested in people, MyoAAV was also used to successfully introduce therapeutic genes into human cells in the lab. This suggests that the early success in animals might hold up in people. The approach also has promise for developing AAVs with potential for targeting other organs, thereby possibly providing treatment for a wide range of genetic conditions.
The new findings are the result of a decade of work from Tabebordbar, the study’s first author. His tireless work is also personal. His father has a rare genetic muscle disease that has put him in a wheelchair. With this latest advance, the hope is that the next generation of promising gene therapies might soon make its way to the clinic to help Tabebordbar’s father and so many other people.
Reference:
[1] Directed evolution of a family of AAV capsid variants enabling potent muscle-directed gene delivery across species. Tabebordbar M, Lagerborg KA, Stanton A, King EM, Ye S, Tellez L, Krunnfusz A, Tavakoli S, Widrick JJ, Messemer KA, Troiano EC, Moghadaszadeh B, Peacker BL, Leacock KA, Horwitz N, Beggs AH, Wagers AJ, Sabeti PC. Cell. 2021 Sep 4:S0092-8674(21)01002-3.
Links:
Muscular Dystrophy Information Page (National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke/NIH)
X-linked myotubular myopathy (Genetic and Rare Diseases Information Center/National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences/NIH)
Somatic Cell Genome Editing (Common Fund/NIH)
Mohammadsharif Tabebordbar (Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard and Harvard University, Cambridge, MA)
Sabeti Lab (Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard and Harvard University)
NIH Support: Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development; Common Fund
The Amazing Brain: Tracking Molecular Events with Calling Cards
Posted on by Dr. Francis Collins
In days mostly gone by, it was fashionable in some circles for people to hand out calling cards to mark their arrival at special social events. This genteel human tradition is now being adapted to the lab to allow certain benign viruses to issue their own high-tech calling cards and mark their arrival at precise locations in the genome. These special locations show where there’s activity involving transcription factors, specialized proteins that switch genes on and off and help determine cell fate.
The idea is that myriad, well-placed calling cards can track brain development over time in mice and detect changes in transcription factor activity associated with certain neuropsychiatric disorders. This colorful image, which won first place in this year’s Show Us Your BRAINs! Photo and Video contest, provides a striking display of these calling cards in action in living brain tissue.
The image comes from Allen Yen, a PhD candidate in the lab of Joseph Dougherty, collaborating with the nearby lab of Rob Mitra. Both labs are located in the Washington University School of Medicine, St. Louis.
Yen and colleagues zoomed in on this section of mouse brain tissue under a microscope to capture dozens of detailed images that they then stitched together to create this high-resolution overview. The image shows neural cells (red) and cell nuclei (blue). But focus in on the neural cells (green) concentrated in the brain’s outer cortex (top) and hippocampus (two lobes in the upper center). They’ve been labelled with calling cards that were dropped off by adeno-associated virus [1].
Once dropped off, a calling card doesn’t bear a pretentious name or title. Rather, the calling card, is a small mobile snippet of DNA called a transposon. It gets dropped off with the other essential component of the technology: a specialized enzyme called a transposase, which the researchers fuse to one of many specific transcription factors of interest.
Each time one of these transcription factors of interest binds DNA to help turn a gene on or off, the attached transposase “grabs” a transposon calling card and inserts it into the genome. As a result, it leaves behind a permanent record of the interaction.
What’s also nice is the calling cards are programmed to give away their general locations. That’s because they encode a fluorescent marker (in this image, it’s a green fluorescent protein). In fact, Yen and colleagues could look under a microscope and tell from all the green that their calling card technology was in place and working as intended.
The final step, though, was to find out precisely where in the genome those calling cards had been left. For this, the researchers used next-generation sequencing to produce a cumulative history and map of each and every calling card dropped off in the genome.
These comprehensive maps allow them to identify important DNA-protein binding events well after the fact. This innovative technology also enables scientists to attribute past molecular interactions with observable developmental outcomes in a way that isn’t otherwise possible.
While the Mitra and Dougherty labs continue to improve upon this technology, it’s already readily adaptable to answer many important questions about the brain and brain disorders. In fact, Yen is now applying the technology to study neurodevelopment in mouse models of neuropsychiatric disorders, specifically autism spectrum disorder (ASD) [2]. This calling card technology also is available for any lab to deploy for studying a transcription factor of interest.
This research is supported by the Brain Research through Advancing Innovative Neurotechnologies® (BRAIN) Initiative. One of the major goals of BRAIN Initiative is to accelerate the development and application of innovative technologies to gain new understanding of the brain. This award-winning image is certainly a prime example of striving to meet this goal. I’ll look forward to what these calling cards will tell us in the future about ASD and other important neurodevelopmental conditions affecting the brain.
References:
[1] A viral toolkit for recording transcription factor-DNA interactions in live mouse tissues. Cammack AJ, Moudgil A, Chen J, Vasek MJ, Shabsovich M, McCullough K, Yen A, Lagunas T, Maloney SE, He J, Chen X, Hooda M, Wilkinson MN, Miller TM, Mitra RD, Dougherty JD. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020 May 5;117(18):10003-10014.
[2] A MYT1L Syndrome mouse model recapitulates patient phenotypes and reveals altered brain development due to disrupted neuronal maturation. Jiayang Chen, Mary E. Lambo, Xia Ge, Joshua T. Dearborn, Yating Liu, Katherine B. McCullough, Raylynn G. Swift, Dora R. Tabachnick, Lucy Tian, Kevin Noguchi, Joel R. Garbow, John N. Constantino. bioRxiv. May 27, 2021.
Links:
Brain Research through Advancing Innovative Neurotechnologies® (BRAIN) Initiative (NIH)
Autism Spectrum Disorder (National Institute of Mental Health/NIH)
Dougherty Lab (Washington University School of Medicine, St. Louis)
Mitra Lab (Washington University School of Medicine)
Show Us Your BRAINs! Photo and Video Contest (BRAIN Initiative/NIH)
NIH Support: National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke; National Institute of Mental Health; National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences; National Human Genome Research Institute; National Institute of General Medical Sciences
More Genetic Clues to COVID-19 Susceptibility and Severity
Posted on by Dr. Francis Collins

Many factors influence our risk of illness from SARS-CoV-2, the coronavirus responsible for COVID-19. That includes being careful to limit our possible exposures to the virus, as well as whether we have acquired immunity from a vaccine or an earlier infection. But once a person is infected, a host of other biological factors, including age and pre-existing medical conditions, will influence one’s risk of becoming severely ill.
While earlier studies have tied COVID-19 severity to genetic variations in a person’s antiviral defenses and blood type, we still have a lot to learn about how a person’s genetic makeup influences COVID-19 susceptibility and severity. So, I was pleased to see the recent findings of an impressive global effort to map the genetic underpinnings of SARS-CoV-2 infection and COVID-19 severity, which involved analyzing the genomes of many thousands of people with COVID-19 around the globe.
This comprehensive search led to the identification of 13 regions of the human genome that appear to play a role in COVID-19 infection or severity. Though more research is needed to sort out these leads, they represent potentially high-quality clues to the pathways that this virus uses to cause illness, and help to explain why some people are more likely to become infected with SARS-CoV-2 or to develop severe disease.
The international effort, known as The COVID-19 Host Genetics Initiative, is led by Andrea Ganna, Institute for Molecular Medicine Finland, Helsinki, and colleagues in the United States and around the world. Teasing out those important genetic influences is no easy task. It requires vast amounts of data, so Ganna reached out to the scientific community via Twitter to announce a new COVID-19 gene-hunting effort and ask for help. Thousands of researchers around the world answered his call. The new study, published in the journal Nature, includes data collected through the initiative as of January 2021, and represents nearly 50,000 COVID-19 patients and another 2 million uninfected controls [1].
In search of common gene variants that may influence who becomes infected with SARS-CoV-2 and how sick they will become, Ganna’s international team turned to genome-wide association studies (GWAS). As part of this, the team analyzed patient genome data for millions of so-called single-nucleotide polymorphisms, or SNPs. While these single “letter” nucleotide substitutions found all across the genome are generally of no health significance, they can point the way to the locations of gene variants that turn up more often in association with particular traits or conditions—in this case, COVID-19 susceptibility or severity. To find them, the researchers compared SNPs in people with COVID-19 to those in about 2 million healthy blood donors from the same population groups. They also looked for variants that turned up significantly more often in people who became severely ill.
Their analyses uncovered a number of gene variants associated with SARS-CoV-2 infection or severe COVID-19 in 13 regions of the human genome, six of which were new. Four of the 13 affect a person’s risk for becoming infected with SARS-CoV-2. The other nine influence a person’s risk for developing severe illness following the infection.
Interestingly, some of these gene variants already were known to have associations with other types of lung or autoimmune diseases. The new findings also help to confirm previous studies suggesting that the gene that determines a person’s blood type may influence a person’s susceptibility to SARS-CoV-2 infection, along with other genes that play a role in immunity. For example, the findings show overlap with variants within a gene called TYK2, which was earlier shown to protect against autoimmune-related diseases. Some of the variants also point to the need for further work to study previously unexplored biological processes that may play potentially important roles in COVID-19.
Two of the new variants associated with disease severity were discovered only by including individuals with East Asian ancestry, highlighting the value of diversity in such analyses to gain a more comprehensive understanding of the biology. One of these newfound variants is close to a gene known as FOXP4, which is especially intriguing because this gene is known to play a role in the airways of the lung.
The researchers continue to look for more underlying clues into the biology of COVID-19. In fact, their latest unpublished analysis has increased the number of COVID-19 patients from about 50,000 to 125,000, making it possible to add another 10 gene variants to the list.
Reference:
[1] Mapping the human genetic architecture of COVID-19. COVID-19 Host Genetics Initiative. Nature. 2021 Jul 8.
Links:
COVID-19 Research (NIH)
Next Page
