dystrophin
Engineering a Better Way to Deliver Therapeutic Genes to Muscles
Posted on by Dr. Francis Collins

Amid all the progress toward ending the COVID-19 pandemic, it’s worth remembering that researchers here and around the world continue to make important advances in tackling many other serious health conditions. As an inspiring NIH-supported example, I’d like to share an advance on the use of gene therapy for treating genetic diseases that progressively degenerate muscle, such as Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD).
As published recently in the journal Cell, researchers have developed a promising approach to deliver therapeutic genes and gene editing tools to muscle more efficiently, thus requiring lower doses [1]. In animal studies, the new approach has targeted muscle far more effectively than existing strategies. It offers an exciting way forward to reduce unwanted side effects from off-target delivery, which has hampered the development of gene therapy for many conditions.
In boys born with DMD (it’s an X-linked disease and therefore affects males), skeletal and heart muscles progressively weaken due to mutations in a gene encoding a critical muscle protein called dystrophin. By age 10, most boys require a wheelchair. Sadly, their life expectancy remains less than 30 years.
The hope is gene therapies will one day treat or even cure DMD and allow people with the disease to live longer, high-quality lives. Unfortunately, the benign adeno-associated viruses (AAVs) traditionally used to deliver the healthy intact dystrophin gene into cells mostly end up in the liver—not in muscles. It’s also the case for gene therapy of many other muscle-wasting genetic diseases.
The heavy dose of viral vector to the liver is not without concern. Recently and tragically, there have been deaths in a high-dose AAV gene therapy trial for X-linked myotubular myopathy (XLMTM), a different disorder of skeletal muscle in which there may already be underlying liver disease, potentially increasing susceptibility to toxicity.
To correct this concerning routing error, researchers led by Mohammadsharif Tabebordbar in the lab of Pardis Sabeti, Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard and Harvard University, Cambridge, MA, have now assembled an optimized collection of AAVs. They have been refined to be about 10 times better at reaching muscle fibers than those now used in laboratory studies and clinical trials. In fact, researchers call them myotube AAVs, or MyoAAVs.
MyoAAVs can deliver therapeutic genes to muscle at much lower doses—up to 250 times lower than what’s needed with traditional AAVs. While this approach hasn’t yet been tried in people, animal studies show that MyoAAVs also largely avoid the liver, raising the prospect for more effective gene therapies without the risk of liver damage and other serious side effects.
In the Cell paper, the researchers demonstrate how they generated MyoAAVs, starting out with the commonly used AAV9. Their goal was to modify the outer protein shell, or capsid, to create an AAV that would be much better at specifically targeting muscle. To do so, they turned to their capsid engineering platform known as, appropriately enough, DELIVER. It’s short for Directed Evolution of AAV capsids Leveraging In Vivo Expression of transgene RNA.
Here’s how DELIVER works. The researchers generate millions of different AAV capsids by adding random strings of amino acids to the portion of the AAV9 capsid that binds to cells. They inject those modified AAVs into mice and then sequence the RNA from cells in muscle tissue throughout the body. The researchers want to identify AAVs that not only enter muscle cells but that also successfully deliver therapeutic genes into the nucleus to compensate for the damaged version of the gene.
This search delivered not just one AAV—it produced several related ones, all bearing a unique surface structure that enabled them specifically to target muscle cells. Then, in collaboration with Amy Wagers, Harvard University, Cambridge, MA, the team tested their MyoAAV toolset in animal studies.
The first cargo, however, wasn’t a gene. It was the gene-editing system CRISPR-Cas9. The team found the MyoAAVs correctly delivered the gene-editing system to muscle cells and also repaired dysfunctional copies of the dystrophin gene better than the CRISPR cargo carried by conventional AAVs. Importantly, the muscles of MyoAAV-treated animals also showed greater strength and function.
Next, the researchers teamed up with Alan Beggs, Boston Children’s Hospital, and found that MyoAAV was effective in treating mouse models of XLMTM. This is the very condition mentioned above, in which very high dose gene therapy with a current AAV vector has led to tragic outcomes. XLMTM mice normally die in 10 weeks. But, after receiving MyoAAV carrying a corrective gene, all six mice had a normal lifespan. By comparison, mice treated in the same way with traditional AAV lived only up to 21 weeks of age. What’s more, the researchers used MyoAAV at a dose 100 times lower than that currently used in clinical trials.
While further study is needed before this approach can be tested in people, MyoAAV was also used to successfully introduce therapeutic genes into human cells in the lab. This suggests that the early success in animals might hold up in people. The approach also has promise for developing AAVs with potential for targeting other organs, thereby possibly providing treatment for a wide range of genetic conditions.
The new findings are the result of a decade of work from Tabebordbar, the study’s first author. His tireless work is also personal. His father has a rare genetic muscle disease that has put him in a wheelchair. With this latest advance, the hope is that the next generation of promising gene therapies might soon make its way to the clinic to help Tabebordbar’s father and so many other people.
Reference:
[1] Directed evolution of a family of AAV capsid variants enabling potent muscle-directed gene delivery across species. Tabebordbar M, Lagerborg KA, Stanton A, King EM, Ye S, Tellez L, Krunnfusz A, Tavakoli S, Widrick JJ, Messemer KA, Troiano EC, Moghadaszadeh B, Peacker BL, Leacock KA, Horwitz N, Beggs AH, Wagers AJ, Sabeti PC. Cell. 2021 Sep 4:S0092-8674(21)01002-3.
Links:
Muscular Dystrophy Information Page (National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke/NIH)
X-linked myotubular myopathy (Genetic and Rare Diseases Information Center/National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences/NIH)
Somatic Cell Genome Editing (Common Fund/NIH)
Mohammadsharif Tabebordbar (Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard and Harvard University, Cambridge, MA)
Sabeti Lab (Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard and Harvard University)
NIH Support: Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development; Common Fund
More Progress Toward Gene Editing for Kids with Muscular Dystrophy
Posted on by Dr. Francis Collins

Thanks to CRISPR and other gene editing technologies, hopes have never been greater for treating or even curing Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) and many other rare, genetic diseases that once seemed tragically out of reach. The latest encouraging news comes from a study in which a single infusion of a CRISPR editing system produced lasting benefits in a mouse model of DMD.
There currently is no way to cure DMD, an ultimately fatal disease that mainly affects boys. Caused by mutations in a gene that codes for a critical protein called dystrophin, DMD progressively weakens the skeletal and heart muscles. People with DMD are usually in wheelchairs by the age of 10, with most dying before the age of 30.
The exquisite targeting ability of CRISPR/Cas9 editing systems rely on a sequence-specific guide RNA to direct a scissor-like, bacterial enzyme (Cas9) to just the right spot in the genome, where it can be used to cut out, replace, or repair disease-causing mutations. In previous studies in mice and dogs, researchers directly infused CRISPR systems directly into the animals bodies. This “in vivo” approach to gene editing successfully restored production of functional dystrophin proteins, strengthening animals’ muscles within weeks of treatment.
But an important question remained: would CRISPR’s benefits persist over the long term? The answer in a mouse model of DMD appears to be “yes,” according to findings published recently in Nature Medicine by Charles Gersbach, Duke University, Durham, NC, and his colleagues [1]. Specifically, the NIH-funded team found that after mice with DMD received one infusion of a specially designed CRISPR/Cas9 system, the abnormal gene was edited in a way that restored dystrophin production in skeletal and heart muscles for more than a year. What’s more, lasting improvements were seen in the structure of the animals’ muscles throughout the same time period.
As exciting as these results may be, much more research is needed to explore both the safety and the efficacy of in vivo gene editing before it can be tried in humans with DMD. For instance, the researchers found that older mice that received the editing system developed an immune response to the bacterially-derived Cas9 protein. However, this response didn’t prevent the CRISPR/Cas9 system from doing its job or appear to cause any adverse effects. Interestingly, younger animals didn’t show such a response.
It’s worth noting that the immune systems of mice and people often respond quite differently. But the findings do highlight some possible challenges of such treatments, as well as approaches to reduce possible side effects. For instance, the latest findings suggest CRISPR/Cas9 treatment might best be done early in life, before an infant’s immune system is fully developed. Also, if it’s necessary to deliver CRISPR/Cas9 to older individuals, it may be beneficial to suppress the immune system temporarily.
Another concern about CRISPR technology is the potential for damaging, “off-target” edits to other parts of the genome. In the new work, the Duke team found that its CRISPR system made very few “off-target” edits. However, the system did make a surprising number of complex edits to the targeted dystrophin gene, including integration of the viral vector used to deliver Cas9. While those editing “errors” might reduce the efficacy of treatment, researchers said they didn’t appear to affect the health of the mice studied.
It’s important to emphasize that this gene editing research aimed at curing DMD is being done in non-reproductive (somatic) cells, primarily muscle tissue. The NIH does not support the use of gene editing technologies in human embryos or human reproductive (germline) cells, which would change the genetic makeup of future offspring.
As such, the Duke researchers’ CRISPR/Cas9 system is designed to work optimally in a range of muscle and muscle-progenitor cells. Still, they were able to detect editing of the dystrophin-producing gene in the liver, kidney, brain, and other tissues. Importantly, there was no evidence of edits in the germline cells of the mice. The researchers note that their CRISPR system can be reconfigured to limit gene editing to mature muscle cells, although that may reduce the treatment’s efficacy.
It’s truly encouraging to see that CRISPR gene editing may confer lasting benefits in an animal model of DMD, but a great many questions remain before trying this new approach in kids with DMD. But that time is coming—so let’s boldly go forth and get answers to those questions on behalf of all who are affected by this heartbreaking disease.
Reference:
[1] Long-term evaluation of AAV-CRISPR genome editing for Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Nelson CE, Wu Y, Gemberling MP, Oliver ML, Waller MA, Bohning JD, Robinson-Hamm JN, Bulaklak K, Castellanos Rivera RM, Collier JH, Asokan A, Gersbach CA. Nat Med. 2019 Feb 18.
Links:
Muscular Dystrophy Information Page (National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke/NIH)
Gersbach Lab (Duke University, Durham, NC)
Somatic Cell Genome Editing (Common Fund/NIH)
NIH Support: National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases; National Institute of Biomedical Imaging and Bioengineering
Gene Editing in Dogs Boosts Hope for Kids with Muscular Dystrophy
Posted on by Dr. Francis Collins
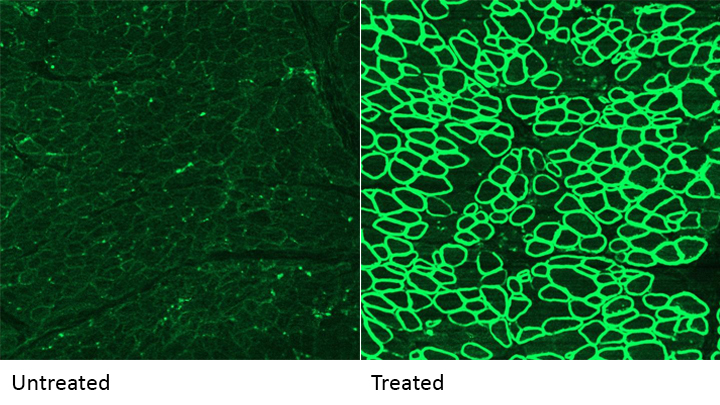
Caption: A CRISPR/cas9 gene editing-based treatment restored production of dystrophin proteins (green) in the diaphragm muscles of dogs with Duchenne muscular dystrophy.
Credit: UT Southwestern
CRISPR and other gene editing tools hold great promise for curing a wide range of devastating conditions caused by misspellings in DNA. Among the many looking to gene editing with hope are kids with Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD), an uncommon and tragically fatal genetic disease in which their muscles—including skeletal muscles, the heart, and the main muscle used for breathing—gradually become too weak to function. Such hopes were recently buoyed by a new study that showed infusion of the CRISPR/Cas9 gene editing system could halt disease progression in a dog model of DMD.
As seen in the micrographs above, NIH-funded researchers were able to use the CRISPR/Cas9 editing system to restore production of a critical protein, called dystrophin, by up to 92 percent in the muscle tissue of affected dogs. While more study is needed before clinical trials could begin in humans, this is very exciting news, especially when one considers that boosting dystrophin levels by as little as 15 percent may be enough to provide significant benefit for kids with DMD.
Gene Editing: Gold Nanoparticle Delivery Shows Promise
Posted on by Dr. Francis Collins
 About a month ago, I had the pleasure of welcoming the Juip (pronounced “Yipe”) family from Michigan to NIH. Although you’d never guess it from this photo, two of the Juip’s five children—9-year-old Claire and 11-year-old Jake (both to my left)—have a rare genetic disease called Friedreich’s ataxia (FA). This inherited condition causes progressive damage to their nervous systems and their hearts. No treatment currently exists for kids like Claire and Jake, yet this remarkable family has turned this serious health challenge into an opportunity to raise awareness about the need for biomedical research.
About a month ago, I had the pleasure of welcoming the Juip (pronounced “Yipe”) family from Michigan to NIH. Although you’d never guess it from this photo, two of the Juip’s five children—9-year-old Claire and 11-year-old Jake (both to my left)—have a rare genetic disease called Friedreich’s ataxia (FA). This inherited condition causes progressive damage to their nervous systems and their hearts. No treatment currently exists for kids like Claire and Jake, yet this remarkable family has turned this serious health challenge into an opportunity to raise awareness about the need for biomedical research.
One thing that helps keep the Juips optimistic is the therapeutic potential of CRISPR/Cas9, an innovative gene editing system that may someday make it possible to correct the genetic mutations responsible for FA and many other conditions. So, I’m sure the Juips were among those encouraged by the recent news that NIH-funded researchers have developed a highly versatile approach to CRISPR/Cas9-based therapies. Instead of relying on viruses to carry the gene-editing system into cells, the new approach uses tiny particles of gold as the delivery system!
