Cavalier King Charles Spaniel
Gene Editing in Dogs Boosts Hope for Kids with Muscular Dystrophy
Posted on by Dr. Francis Collins
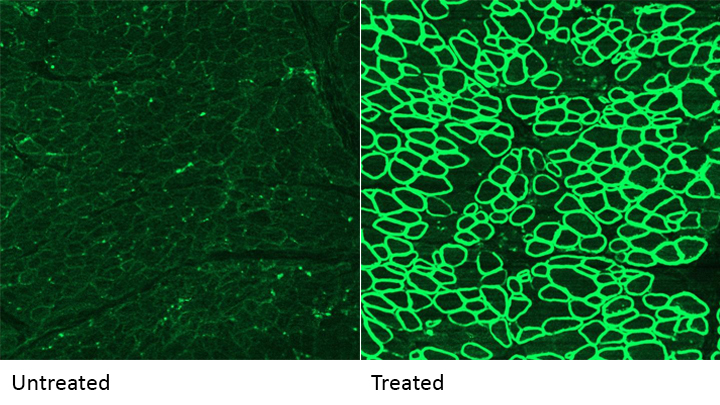
Caption: A CRISPR/cas9 gene editing-based treatment restored production of dystrophin proteins (green) in the diaphragm muscles of dogs with Duchenne muscular dystrophy.
Credit: UT Southwestern
CRISPR and other gene editing tools hold great promise for curing a wide range of devastating conditions caused by misspellings in DNA. Among the many looking to gene editing with hope are kids with Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD), an uncommon and tragically fatal genetic disease in which their muscles—including skeletal muscles, the heart, and the main muscle used for breathing—gradually become too weak to function. Such hopes were recently buoyed by a new study that showed infusion of the CRISPR/Cas9 gene editing system could halt disease progression in a dog model of DMD.
As seen in the micrographs above, NIH-funded researchers were able to use the CRISPR/Cas9 editing system to restore production of a critical protein, called dystrophin, by up to 92 percent in the muscle tissue of affected dogs. While more study is needed before clinical trials could begin in humans, this is very exciting news, especially when one considers that boosting dystrophin levels by as little as 15 percent may be enough to provide significant benefit for kids with DMD.
