epigenetics
New Technology Opens Evolutionary Window into Brain Development
Posted on by Dr. Francis Collins

One of the great mysteries in biology is how we humans ended up with such large, complex brains. In search of clues, researchers have spent years studying the protein-coding genes activated during neurodevelopment. But some answers may also be hiding in non-coding regions of the human genome, where sequences called regulatory elements increase or decrease the activity of genes.
A fascinating example involves a type of regulatory element called a human accelerated region (HAR). Although “human” is part of this element’s name, it turns out that the genomes of all vertebrates—not just humans—contain the DNA segments now designated as HARs.
In most organisms, HARs show a relatively low rate of mutation, which means these regulatory elements have been highly conserved across species throughout evolutionary time [1]. The big exception is Homo sapiens, in which HARs have exhibited a much higher rate of mutations.
The accelerated rate of HARs mutations observed in humans suggest that, over the course of very long periods of time, these genomic changes might have provided our species with some sort of evolutionary advantage. What might that be? Many have speculated the advantage might involve the brain because HARs are often associated with genes involved in neurodevelopment. Now, in a paper published in the journal Neuron, an NIH-supported team confirms that’s indeed the case [2].
In the new work, researchers found that about half of the HARs in the human genome influence the activity, or expression, of protein-coding genes in neural cells and tissues during the brain’s development [3]. The researchers say their study—the most comprehensive to date of the 3,171 HARs in the human genome—firmly establishes that this type of regulatory element helps to drive patterns of neurodevelopmental gene activity specific to humans.
Yet to be determined is precisely how HARs affect the development of the human brain. The quest to uncover these details will no doubt shed new light on fundamental questions about the brain, its billions of neurons, and their trillions of interconnections. For example, why does human neural development span decades, longer than the life spans of most primates and other mammals? Answering such questions could also reveal new clues into a range of cognitive and behavioral disorders. In fact, early research has already made tentative links between HARs and neurodevelopmental conditions such as autism spectrum disorder and schizophrenia [3].
The latest work was led by Kelly Girskis, Andrew Stergachis, and Ellen DeGennaro, all of whom were in the lab of Christopher Walsh while working on the project. An NIH grantee, Walsh is director of the Allen Discovery Center for Brain Evolution at Boston Children’s Hospital and Harvard Medical School, which is supported by the Paul G. Allen Foundation Frontiers Group, and is an Investigator of the Howard Hughes Medical Institute.
Though HARs have been studied since 2006, one of the big challenges in systematically assessing them has been technological. The average length of a HAR is about 269 bases of DNA, but current technologies for assessing function can only easily analyze DNA molecules that span 150 bases or less.
Ryan Doan, who was then in the Walsh Lab, and his colleagues solved the problem by creating a new machine called CaptureMPRA. (MPRA is short for “massively parallel reporter assays.”) This technological advance cleverly barcodes HARs and, more importantly, makes it possible to analyze HARs up to about 500 bases in length.
Using CaptureMPRA technology in tandem with cell culture studies, researchers rolled up their sleeves and conducted comprehensive, full-sequence analyses of more than 3,000 HARs. In their initial studies, primarily in neural cells, they found nearly half of human HARs are active to drive gene expression in cell culture. Of those, 42 percent proved to have increased ability to enhance gene expression compared to their orthologues, or counterparts, in chimpanzees.
Next, the team integrated these data with an existing epigenetic dataset derived from developing human brain cells, as well as additional datasets generated from sorted brain cell types. They found that many HARs appeared to have the ability to increase the activity of protein-coding genes, while a smaller—but very significant—subset of the HARs appeared to be enhancing gene expression specifically in neural progenitor cells, which are responsible for making various neural cell types.
The data suggest that as the human HAR sequences mutated and diverged from other mammals, they increased their ability to enhance or sometimes suppress the activity of certain genes in neural cells. To illustrate this point, the researchers focused on two HARs that appear to interact specifically with a gene referred to as R17. This gene can have highly variable gene expression patterns not only in different human cell types, but also in cells from other vertebrates and non-vertebrates.
In the human cerebral cortex, the outermost part of the brain that’s responsible for complex behaviors, R17 is expressed only in neural progenitor cells and only at specific time points. The researchers found that R17 slows the progression of neural progenitor cells through the cell cycle. That might seem strange, given the billions of neurons that need to be made in the cortex. But it’s consistent with the biology. In the human, it takes more than 130 days for the cortex to complete development, compared to about seven days in the mouse.
Clearly, to learn more about how the human brain evolved, researchers will need to look for clues in many parts of the genome at once, including its non-coding regions. To help researchers navigate this challenging terrain, the Walsh team has created an online resource displaying their comprehensive HAR data. It will appear soon, under the name HAR Hub, on the University of California Santa Cruz Genome Browser.
References:
[1] An RNA gene expressed during cortical development evolved rapidly in humans. Pollard KS, Salama SR, Lambert N, Lambot MA, Coppens S, Pedersen JS, Katzman S, King B, Onodera C, Siepel A, Kern AD, Dehay C, Igel H, Ares M Jr, Vanderhaeghen P, Haussler D. Nature. 2006 Sep 14;443(7108):167-72.
[2] Rewiring of human neurodevelopmental gene regulatory programs by human accelerated regions. Girskis KM, Stergachis AB, DeGennaro EM, Doan RN, Qian X, Johnson MB, Wang PP, Sejourne GM, Nagy MA, Pollina EA, Sousa AMM, Shin T, Kenny CJ, Scotellaro JL, Debo BM, Gonzalez DM, Rento LM, Yeh RC, Song JHT, Beaudin M, Fan J, Kharchenko PV, Sestan N, Greenberg ME, Walsh CA. Neuron. 2021 Aug 25:S0896-6273(21)00580-8.
[3] Mutations in human accelerated regions disrupt cognition and social behavior. Doan RN, Bae BI, Cubelos B, Chang C, Hossain AA, Al-Saad S, Mukaddes NM, Oner O, Al-Saffar M, Balkhy S, Gascon GG; Homozygosity Mapping Consortium for Autism, Nieto M, Walsh CA. Cell. 2016 Oct 6;167(2):341-354.
Links:
Christopher Walsh Laboratory (Boston Children’s Hospital and Harvard Medical School)
The Paul G. Allen Foundation Frontiers Group (Seattle)
NIH Support: National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke; National Institute of Mental Health; National Institute of General Medical Sciences; National Cancer Institute
First Comprehensive Census of Cell Types in Brain Area Controlling Movement
Posted on by Dr. Francis Collins

The primary motor cortex is the part of the brain that enables most of our skilled movements, whether it’s walking, texting on our phones, strumming a guitar, or even spiking a volleyball. The region remains a major research focus, and that’s why NIH’s Brain Research Through Advancing Innovative Neurotechnologies® (BRAIN) Initiative – Cell Census Network (BICCN) has just unveiled two groundbreaking resources: a complete census of cell types present in the mammalian primary motor cortex, along with the first detailed atlas of the region, located along the back of the frontal lobe in humans (purple stripe above).
This remarkably comprehensive work, detailed in a flagship paper and more than a dozen associated articles published in the journal Nature, promises to vastly expand our understanding of the primary motor cortex and how it works to keep us moving [1]. The papers also represent the collaborative efforts of more than 250 BICCN scientists from around the world, teaming up over many years.
Started in 2013, the BRAIN Initiative is an ambitious project with a range of groundbreaking goals, including the creation of an open-access reference atlas that catalogues all of the brain’s many billions of cells. The primary motor cortex was one of the best places to get started on assembling an atlas because it is known to be well conserved across mammalian species, from mouse to human. There’s also a rich body of work to aid understanding of more precise cell-type information.
Taking advantage of recent technological advances in single-cell analysis, the researchers categorized into different types the millions of neurons and other cells in this brain region. They did so on the basis of morphology, or shape, of the cells, as well as their locations and connections to other cells. The researchers went even further to characterize and sort cells based on: their complex patterns of gene expression, the presence or absence of chemical (or epigenetic) marks on their DNA, the way their chromosomes are packaged into chromatin, and their electrical properties.
The new data and analyses offer compelling evidence that neural cells do indeed fall into distinct types, with a high degree of correspondence across their molecular genetic, anatomical, and physiological features. These findings support the notion that neural cells can be classified into molecularly defined types that are also highly conserved or shared across mammalian species.
So, how many cell types are there? While that’s an obvious question, it doesn’t have an easy answer. The number varies depending upon the method used for sorting them. The researchers report that they have identified about 25 classes of cells, including 16 different neuronal classes and nine non-neuronal classes, each composed of multiple subtypes of cells.
These 25 classes were determined by their genetic profiles, their locations, and other characteristics. They also showed up consistently across species and using different experimental approaches, suggesting that they have important roles in the neural circuitry and function of the motor cortex in mammals.
Still, many precise features of the cells don’t fall neatly into these categories. In fact, by focusing on gene expression within single cells of the motor cortex, the researchers identified more potentially important cell subtypes, which fall into roughly 100 different clusters, or distinct groups. As scientists continue to examine this brain region and others using the latest new methods and approaches, it’s likely that the precise number of recognized cell types will continue to grow and evolve a bit.
This resource will now serve as a springboard for future research into the structure and function of the brain, both within and across species. The datasets already have been organized and made publicly available for scientists around the world.
The atlas also now provides a foundation for more in-depth study of cell types in other parts of the mammalian brain. The BICCN is already engaged in an effort to generate a brain-wide cell atlas in the mouse, and is working to expand coverage in the atlas for other parts of the human brain.
The cell census and atlas of the primary motor cortex are important scientific advances with major implications for medicine. Strokes commonly affect this region of the brain, leading to partial or complete paralysis of the opposite side of the body.
By considering how well cell census information aligns across species, scientists also can make more informed choices about the best models to use for deepening our understanding of brain disorders. Ultimately, these efforts and others underway will help to enable precise targeting of specific cell types and to treat a wide range of brain disorders that affect thinking, memory, mood, and movement.
Reference:
[1] A multimodal cell census and atlas of the mammalian primary motor cortex. BRAIN Initiative Cell Census Network (BICCN). Nature. Oct 6, 2021.
Links:
NIH Brain Research Through Advancing Innovative Neurotechnologies® (BRAIN) Initiative (NIH)
BRAIN Initiative – Cell Census Network (BICCN) (NIH)
NIH Support: National Institute of Mental Health; National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke
Mood-Altering Messenger Goes Nuclear
Posted on by Dr. Francis Collins
Serotonin is best known for its role as a chemical messenger in the brain, helping to regulate mood, appetite, sleep, and many other functions. It exerts these influences by binding to its receptor on the surface of neural cells. But startling new work suggests the impact of serotonin does not end there: the molecule also can enter a cell’s nucleus and directly switch on genes.
While much more study is needed, this is a potentially groundbreaking discovery. Not only could it have implications for managing depression and other mood disorders, it may also open new avenues for treating substance abuse and neurodegenerative diseases.
To understand how serotonin contributes to switching genes on and off, a lesson on epigenetics is helpful. Keep in mind that the DNA instruction book of all cells is essentially the same, yet the chapters of the book are read in very different ways by cells in different parts of the body. Epigenetics refers to chemical marks on DNA itself or on the protein “spools” called histones that package DNA. These marks influence the activity of genes in a particular cell without changing the underlying DNA sequence, switching them on and off or acting as “volume knobs” to turn the activity of particular genes up or down.
The marks include various chemical groups—including acetyl, phosphate, or methyl—which are added at precise locations to those spool-like proteins called histones. The addition of such groups alters the accessibility of the DNA for copying into messenger RNA and producing needed proteins.
In the study reported in Nature, researchers led by Ian Maze and postdoctoral researcher Lorna Farrelly, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, followed a hunch that serotonin molecules might also get added to histones [1]. There had been hints that it might be possible. For instance, earlier evidence suggested that inside cells, serotonin could enter the nucleus. There also was evidence that serotonin could attach to proteins outside the nucleus in a process called serotonylation.
These data begged the question: Is serotonylation important in the brain and/or other living tissues that produce serotonin in vivo? After a lot of hard work, the answer now appears to be yes.
These NIH-supported researchers found that serotonylation does indeed occur in the cell nucleus. They also identified a particular enzyme that directly attaches serotonin molecules to histone proteins. With serotonin attached, DNA loosens on its spool, allowing for increased gene expression.
The team found that histone serotonylation takes place in serotonin-producing human neurons derived from induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs). They also observed this process occurring in the brains of developing mice.
In fact, the researchers found evidence of those serotonin marks in many parts of the body. They are especially prevalent in the brain and gut, where serotonin also is produced in significant amounts. Those marks consistently correlate with areas of active gene expression.
The serotonin mark often occurs on histones in combination with a second methyl mark. The researchers suggest that this double marking of histones might help to further reinforce an active state of gene expression.
This work demonstrates that serotonin can directly influence gene expression in a manner that’s wholly separate from its previously known role in transmitting chemical messages from one neuron to the next. And, there are likely other surprises in store.
The newly discovered role of serotonin in modifying gene expression may contribute significantly to our understanding of mood disorders and other psychiatric conditions with known links to serotonin signals, suggesting potentially new targets for therapeutic intervention. But for now, this fundamental discovery raises many more intriguing questions than it answers.
Science is full of surprises, and this paper is definitely one of them. Will this kind of histone marking occur with other chemical messengers, such as dopamine and acetylcholine? This unexpected discovery now allows us to track serotonin and perhaps some of the brain’s other chemical messengers to see what they might be doing in the cell nucleus and whether this information might one day help in treating the millions of Americans with mood and behavioral disorders.
Reference:
[1] Histone serotonylation is a permissive modification that enhances TFIID binding to H3K4me3. Farrelly LA, Thompson RE, Zhao S, Lepack AE, Lyu Y, Bhanu NV, Zhang B, Loh YE, Ramakrishnan A, Vadodaria KC, Heard KJ, Erikson G, Nakadai T, Bastle RM, Lukasak BJ, Zebroski H 3rd, Alenina N, Bader M, Berton O, Roeder RG, Molina H, Gage FH, Shen L, Garcia BA, Li H, Muir TW, Maze I. Nature. 2019 Mar 13. [Epub ahead of print]
Links:
Any Mood Disorder (National Institute of Mental Health/NIH)
Drugs, Brains, and Behavior: The Science of Addiction (National Institute on Drug Abuse/NIH)
Epigenomics (National Human Genome Research Institute/NIH)
Maze Lab (Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, NY)
NIH Support: National Institute on Drug Abuse; National Institute of Mental Health; National Institute of General Medical Sciences; National Cancer Institute
Creative Minds: A New Way to Look at Cancer
Posted on by Dr. Francis Collins
Inside our cells, strands of DNA wrap around spool-like histone proteins to form a DNA-histone complex called chromatin. Bradley Bernstein, a pathologist at Massachusetts General Hospital, Harvard University, and Broad Institute, has always been fascinated by this process. What interests him is the fact that an approximately 6-foot-long strand of DNA can be folded and packed into orderly chromatin structures inside a cell nucleus that’s just 0.0002 inch wide.
Bernstein’s fascination with DNA packaging led to the recent major discovery that, when chromatin misfolds in brain cells, it can activate a gene associated with the cancer glioma [1]. This suggested a new cancer-causing mechanism that does not require specific DNA mutations. Now, with a 2016 NIH Director’s Pioneer Award, Bernstein is taking a closer look at how misfolded and unstable chromatin can drive tumor formation, and what that means for treating cancer.
Creative Minds: A New Mechanism for Epigenetics?
Posted on by Dr. Francis Collins
To learn more about how DNA and inheritance works, Keith Maggert has spent much of his nearly 30 years as a researcher studying what takes place not just within the DNA genome but also the subtle modifications of it. That’s where a stable of enzymes add chemical marks to DNA, turning individual genes on or off without changing their underlying sequence. What’s really intrigued Maggert is these “epigenetic” modifications are maintained through cell division and can even get passed down from parent to child over many generations. Like many researchers, he wants to know how it happens.
Maggert thinks there’s more to the story than scientists have realized. Now an associate professor at the University of Arizona College of Medicine, Tucson, he suspects that a prominent subcellular structure in the nucleus called the nucleolus also exerts powerful epigenetic effects. What’s different about the nucleolus, Maggert proposes, is it doesn’t affect genes one by one, a focal point of current epigenetic research. He thinks under some circumstances its epigenetic effects can activate many previously silenced, or “off” genes at once, sending cells and individuals on a different path toward health or disease.
Maggert has received a 2016 NIH Director’s Transformative Research Award to pursue this potentially new paradigm. If correct, it would transform current thinking in the field and provide an exciting new perspective to track epigenetics and its contributions to a wide range of human diseases, including cancer, cardiovascular disease, and neurodegenerative disorders.
Precision Oncology: Epigenetic Patterns Predict Glioblastoma Outcomes
Posted on by Dr. Francis Collins

Caption: Oncologists review a close-up image of a brain tumor (green dot).
Credit: National Cancer Institute
Scientists have spent much time and energy mapping the many DNA misspellings that can transform healthy cells into cancerous ones. But recently it has become increasingly clear that changes to the DNA sequence itself are not the only culprits. Cancer can also be driven by epigenetic changes to DNA—modifications to chemical marks on the genome don’t alter the sequence of the DNA molecule, but act to influence gene activity. A prime example of this can been seen in glioblastoma, a rare and deadly form of brain cancer that strikes about 12,000 Americans each year.
In fact, an NIH-funded research team recently published in Nature Communications the most complete portrait to date of the epigenetic patterns characteristic of the glioblastoma genome [1]. Among their findings were patterns associated with how long patients survived after the cancer was detected. While far more research is needed, the findings highlight the potential of epigenetic information to help doctors devise more precise ways of diagnosing, treating, and perhaps even preventing glioblastoma and many other forms of cancer.
Creative Minds: Building the RNA Toolbox
Posted on by Dr. Francis Collins
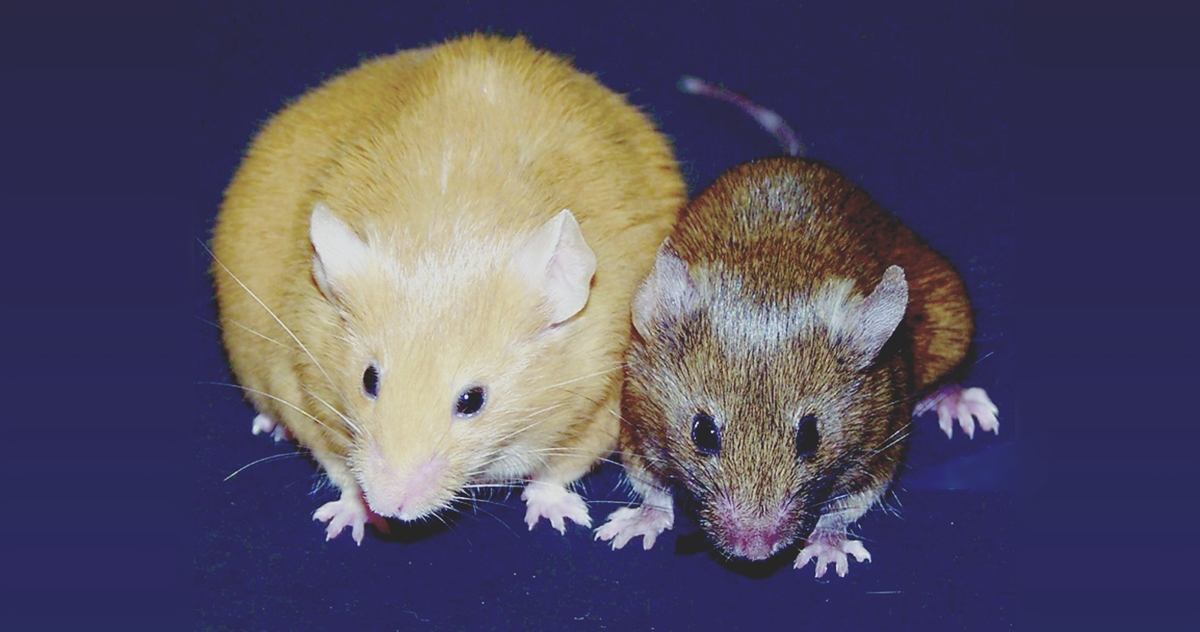

Caption: Genetically identical mice. The Agouti gene is active in the yellow mouse and inactive in the brown mouse.
Credit: Dana Dolinoy, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, and Randy Jirtle, Duke University, Durham, NC
Step inside the lab of Dana Dolinoy at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, and you’re sure to hear conversations that include the rather strange word “agouti” (uh-goo-tee). In this context, it’s a name given to a strain of laboratory mice that arose decades ago from a random mutation in the Agouti gene, which is normally expressed only transiently in hair follicles. The mutation causes the gene to be turned on, or expressed, continuously in all cell types, producing mice that are yellow, obese, and unusually prone to developing diabetes and cancer. As it turns out, these mutant mice and the gene they have pointed to are more valuable than ever today because they offer Dolinoy and other researchers an excellent model for studying the rapidly emerging field of epigenomics.
The genome of the mouse, just as for the human, is the complete DNA instruction book; it contains the coding information for building the proteins that carry out a variety of functions in a cell. But modifications to the DNA determine its function, and these are collectively referred to as the epigenome. The epigenome is made up of chemical tags and proteins that can attach to the DNA and direct such actions as turning genes on or off, thereby controlling the production of proteins in particular cells. These tags have different patterns in each cell type, helping to explain, for example, why a kidney and a skin cell can behave so differently when they share the same DNA.
Some types of genes, including Agouti, are particularly vulnerable to epigenomic effects. In fact, Dolinoy has discovered that exposing normal, wild-type (brown) mice to certain chemicals and dietary factors during pregnancy can switch on the Agouti gene in their developing offspring, turning their coats yellow and their health poor. Dolinoy says these experiments raise much larger questions: If researchers discover populations of humans that have been exposed to lifestyle or environmental factors that modify their epigenomes in ways that may possibly contribute to risk for certain diseases, can the modification be passed on to their children and grandchildren (referred to as transgenerational epigenetic inheritance, a controversial topic)? If so, how can we develop the high-precision tools needed to better understand and perhaps even reduce such risks? The University of Michigan researcher received a 2015 NIH Director’s Transformative Research Award to undertake that challenge.
Largest Study Yet Shows Mother’s Smoking Changes Baby’s Epigenome
Posted on by Dr. Francis Collins

Credit: Daniel Berehulak/Getty Images
Despite years of public health campaigns warning of the dangers of smoking when pregnant, many women are unaware of the risk or find themselves unable to quit. As a result, far too many babies are still being exposed in the womb to toxins that enter their mothers’ bloodstreams when they inhale cigarette smoke. Among the many infant and child health problems that have been linked to maternal smoking are premature birth, low birth weight, asthma, reduced lung function, sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS), and cleft lip and/or palate.
Now, a large international study involving NIH-supported researchers provides a biological mechanism that may explain how exposure to cigarette toxins during fetal development can produce these health problems [1]. That evidence centers on the impact of the toxins on the epigenome of the infant’s body tissues. The epigenome refers to chemical modifications of DNA (particularly methylation of cytosines), as well as proteins that bind to DNA and affect its function. The genome of an individual is the same in all cells of their body, but the epigenome determines whether genes are turned on or off in particular cells. The study found significant differences between the epigenetic patterns of babies born to women who smoked during pregnancy and those born to non-smokers, with many of the differences affecting genes known to play key roles in the development of the lungs, face, and nervous system.
Hitting the Right Target? Lab Studies Suggest Epigenetic Drug May Fight Childhood Brain Cancer
Posted on by Dr. Francis Collins

Caption: Remembering a few of the many children who’ve died of DIPG; Left, Lyla Nsouli and parents; upper right, Andrew Smith and mom; lower right, Alexis Agin and parents.
Credits: Nsouli, Smith, and Agin families
Every year in the United States, several hundred children and their families receive a devastating diagnosis: diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma (DIPG). Sadly, this inoperable tumor of the brain stem, little known by the public, is almost always fatal, and efforts to develop life-saving treatments have been hampered by a lack of molecular data to identify agents that might specifically target DIPG. In fact, more than 200 clinical trials of potential drugs have been conducted in DIPG patients without any success.
Now, using cell lines and mouse models created with tumor tissue donated by 16 DIPG patients, an international research coalition has gained a deeper understanding of this childhood brain cancer at the molecular level. These new preclinical tools have also opened the door to identifying more precise targets for DIPG therapy, including the exciting possibility of using a drug already approved for another type of cancer.
Next Page