lungs
Clinical Center Doctors Testing 3D-Printed Miniature Ventilator
Posted on by James K. Gilman, MD, NIH Clinical Center

Here at the NIH Clinical Center, we are proud to be considered a world-renowned research hospital that provides hope through pioneering clinical research to improve human health. But what you may not know is that our doctors are constantly partnering with public and private sectors to come up with innovative technologies that will help to advance health outcomes.
I’m excited to bring to you a story that is perfect example of the ingenuity of our NIH doctors working with global strategic partners to create potentially life-saving technologies. This story begins during the COVID-19 pandemic with the global shortage of ventilators to help patients breathe. Hospitals had a profound need for inexpensive, easy-to-use, rapidly mass-produced resuscitation devices that could be quickly distributed in areas of critical need.
Through strategic partnerships, our Clinical Center doctors learned about and joined an international group of engineers, physicians, respiratory therapists, and patient advocates using their engineering skills to create a ventilator that was functional, affordable, and intuitive. After several iterations and bench testing, they devised a user-friendly ventilator.
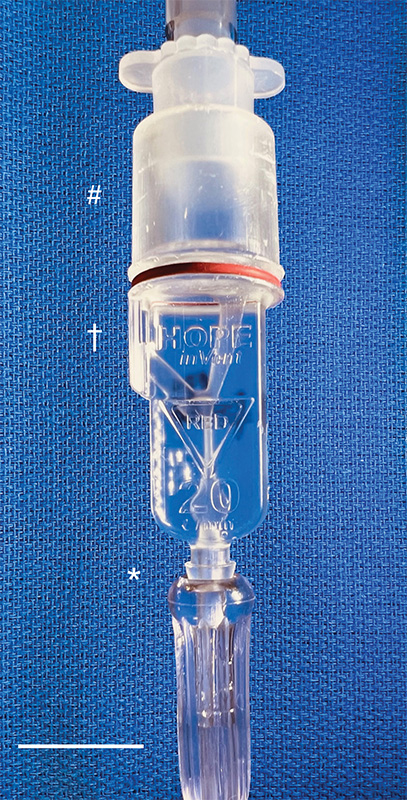
Then, with the assistance of 3D-printing technology, they improved the original design and did something pretty incredible: the team created the smallest single-patient ventilator seen to date. The device is just 2.4 centimeters (about 1 inch) in diameter with a length of 7.4 centimeters (about 3 inches).
A typical ventilator in a hospital obviously is much larger and has a bellows system. It fills with oxygen and then forces it into the lungs followed by the patient passively exhaling. These systems have multiple moving parts, valves, hoses, and electronic or mechanical controls to manage all aspects of the oxygen flow into the lungs.
But our miniature, 3D-printed ventilator is single use, disposable, and has no moving parts. It’s based on principles of fluidics to ventilate patients by automatically oscillating between forced inspiration and assisted expiration as airway pressure changes. It requires only a continuous supply of pressurized oxygen.
The possibilities of this 3D-printed miniature ventilator are broad. The ventilators could be easily used in emergency transport, potentially treating battlefield casualties or responding to disasters and mass casualty events like earthquakes.
While refining a concept is important, the key is converting it to actual use, which our doctors are doing admirably in their preclinical and clinical studies. NIH’s William Pritchard, Andrew Mannes, Brad Wood, John Karanian, Ivane Bakhutashvili, Matthew Starost, David Eckstein, and medical student Sheridan Reed studied and have already tested the ventilators in swine with acute lung injury, a common severe outcome in a number of respiratory threats including COVID-19.
In the study, the doctors tested three versions of the device built to correspond to mild, moderate, and severe lung injury. The respirators provided adequate support for moderate and mild lung injuries, and the doctors recall how amazing it was initially to witness a 190-pound swine ventilated by this miniature ventilator.
The doctors believe that the 3D-printed miniature ventilator is a potential “game changer” from start to finish since it is lifesaving, small, simple to use, can be easily and inexpensively printed and stored, and does not require additional maintenance. They recently published their preclinical trial results in the journal Science Translational Medicine [1].
The NIH team is preparing to initiate first-in-human trials here at the Clinical Center in the coming months. Perhaps, in the not-too-distant future, a device designed to help people breathe could fit into your pocket next to your phone and keys.
Reference:
[1] In-line miniature 3D-printed pressure-cycled ventilator maintains respiratory homeostasis in swine with induced acute pulmonary injury. Pritchard WF, Karanian JW, Jung C, Bakhutashvili I, Reed SL, Starost MF, Froelke BR, Barnes TR, Stevenson D, Mendoza A, Eckstein DJ, Wood BJ, Walsh BK, Mannes AJ. Sci Transl Med. 2022 Oct 12;14(666):eabm8351.
Links:
Clinical Center (NIH)
Andrew Mannes (Clinical Center)
Bradford Wood (Clinical Center)
David Eckstein (Clinical Center)
Note: Dr. Lawrence Tabak, who performs the duties of the NIH Director, has asked the heads of NIH’s Institutes and Centers (ICs) to contribute occasional guest posts to the blog to highlight some of the interesting science that they support and conduct. This is the 21st in the series of NIH IC guest posts that will run until a new permanent NIH director is in place.
Millions of Single-Cell Analyses Yield Most Comprehensive Human Cell Atlas Yet
Posted on by Lawrence Tabak, D.D.S., Ph.D.

There are 37 trillion or so cells in our bodies that work together to give us life. But it may surprise you that we still haven’t put a good number on how many distinct cell types there are within those trillions of cells.
That’s why in 2016, a team of researchers from around the globe launched a historic project called the Human Cell Atlas (HCA) consortium to identify and define the hundreds of presumed distinct cell types in our bodies. Knowing where each cell type resides in the body, and which genes each one turns on or off to create its own unique molecular identity, will revolutionize our studies of human biology and medicine across the board.
Since its launch, the HCA has progressed rapidly. In fact, it has already reached an important milestone with the recent publication in the journal Science of four studies that, together, comprise the first multi-tissue drafts of the human cell atlas. This draft, based on analyses of millions of cells, defines more than 500 different cell types in more than 30 human tissues. A second draft, with even finer definition, is already in the works.
Making the HCA possible are recent technological advances in RNA sequencing. RNA sequencing is a topic that’s been mentioned frequently on this blog in a range of research areas, from neuroscience to skin rashes. Researchers use it to detect and analyze all the messenger RNA (mRNA) molecules in a biological sample, in this case individual human cells from a wide range of tissues, organs, and individuals who voluntarily donated their tissues.
By quantifying these RNA messages, researchers can capture the thousands of genes that any given cell actively expresses at any one time. These precise gene expression profiles can be used to catalogue cells from throughout the body and understand the important similarities and differences among them.
In one of the published studies, funded in part by the NIH, a team co-led by Aviv Regev, a founding co-chair of the consortium at the Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard, Cambridge, MA, established a framework for multi-tissue human cell atlases [1]. (Regev is now on leave from the Broad Institute and MIT and has recently moved to Genentech Research and Early Development, South San Francisco, CA.)
Among its many advances, Regev’s team optimized single-cell RNA sequencing for use on cell nuclei isolated from frozen tissue. This technological advance paved the way for single-cell analyses of the vast numbers of samples that are stored in research collections and freezers all around the world.
Using their new pipeline, Regev and team built an atlas including more than 200,000 single-cell RNA sequence profiles from eight tissue types collected from 16 individuals. These samples were archived earlier by NIH’s Genotype-Tissue Expression (GTEx) project. The team’s data revealed unexpected differences among cell types but surprising similarities, too.
For example, they found that genetic profiles seen in muscle cells were also present in connective tissue cells in the lungs. Using novel machine learning approaches to help make sense of their data, they’ve linked the cells in their atlases with thousands of genetic diseases and traits to identify cell types and genetic profiles that may contribute to a wide range of human conditions.
By cross-referencing 6,000 genes previously implicated in causing specific genetic disorders with their single-cell genetic profiles, they identified new cell types that may play unexpected roles. For instance, they found some non-muscle cells that may play a role in muscular dystrophy, a group of conditions in which muscles progressively weaken. More research will be needed to make sense of these fascinating, but vital, discoveries.
The team also compared genes that are more active in specific cell types to genes with previously identified links to more complex conditions. Again, their data surprised them. They identified new cell types that may play a role in conditions such as heart disease and inflammatory bowel disease.
Two of the other papers, one of which was funded in part by NIH, explored the immune system, especially the similarities and differences among immune cells that reside in specific tissues, such as scavenging macrophages [2,3] This is a critical area of study. Most of our understanding of the immune system comes from immune cells that circulate in the bloodstream, not these resident macrophages and other immune cells.
These immune cell atlases, which are still first drafts, already provide an invaluable resource toward designing new treatments to bolster immune responses, such as vaccines and anti-cancer treatments. They also may have implications for understanding what goes wrong in various autoimmune conditions.
Scientists have been working for more than 150 years to characterize the trillions of cells in our bodies. Thanks to this timely effort and its advances in describing and cataloguing cell types, we now have a much better foundation for understanding these fundamental units of the human body.
But the latest data are just the tip of the iceberg, with vast flows of biological information from throughout the human body surely to be released in the years ahead. And while consortium members continue making history, their hard work to date is freely available to the scientific community to explore critical biological questions with far-reaching implications for human health and disease.
References:
[1] Single-nucleus cross-tissue molecular reference maps toward understanding disease gene function. Eraslan G, Drokhlyansky E, Anand S, Fiskin E, Subramanian A, Segrè AV, Aguet F, Rozenblatt-Rosen O, Ardlie KG, Regev A, et al. Science. 2022 May 13;376(6594):eabl4290.
[2] Cross-tissue immune cell analysis reveals tissue-specific features in humans. Domínguez Conde C, Xu C, Jarvis LB, Rainbow DB, Farber DL, Saeb-Parsy K, Jones JL,Teichmann SA, et al. Science. 2022 May 13;376(6594):eabl5197.
[3] Mapping the developing human immune system across organs. Suo C, Dann E, Goh I, Jardine L, Marioni JC, Clatworthy MR, Haniffa M, Teichmann SA, et al. Science. 2022 May 12:eabo0510.
Links:
Ribonucleic acid (RNA) (National Human Genome Research Institute/NIH)
Studying Cells (National Institute of General Medical Sciences/NIH)
Regev Lab (Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard, Cambridge, MA)
NIH Support: Common Fund; National Cancer Institute; National Human Genome Research Institute; National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute; National Institute on Drug Abuse; National Institute of Mental Health; National Institute on Aging; National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases; National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke; National Eye Institute
‘Decoy’ Protein Works Against Multiple Coronavirus Variants in Early Study
Posted on by Lawrence Tabak, D.D.S., Ph.D.
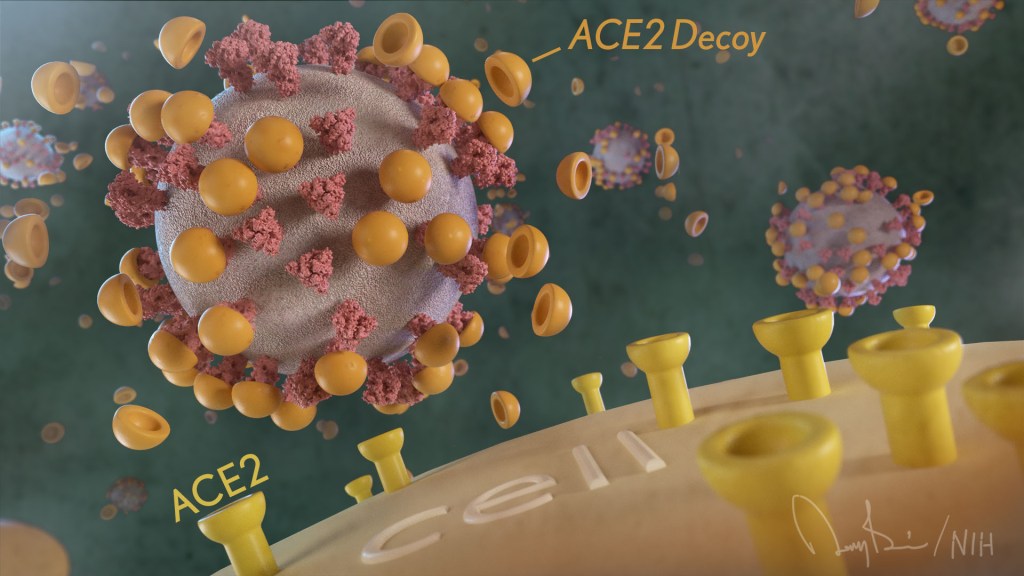
The NIH continues to support the development of some very innovative therapies to control SARS-CoV-2, the coronavirus that causes COVID-19. One innovative idea involves a molecular decoy to thwart the coronavirus.
How’s that? The decoy is a specially engineered protein particle that mimics the 3D structure of the ACE2 receptor, a protein on the surface of our cells that the virus’s spike proteins bind to as the first step in causing an infection.
The idea is when these ACE2 decoys are administered therapeutically, they will stick to the spike proteins that crown the coronavirus (see image above). With its spikes covered tightly in decoy, SARS-CoV-2 has a more-limited ability to attach to the real ACE2 and infect our cells.
Recently, the researchers published their initial results in the journal Nature Chemical Biology, and the early data look promising [1]. They found in mouse models of severe COVID-19 that intravenous infusion of an engineered ACE2 decoy prevented lung damage and death. Though more study is needed, the researchers say the decoy therapy could potentially be delivered directly to the lungs through an inhaler and used alone or in combination with other COVID-19 treatments.
The findings come from a research team at the University of Illinois Chicago team, led by Asrar Malik and Jalees Rehman, working in close collaboration with their colleagues at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign. The researchers had been intrigued by an earlier clinical trial testing the ACE2 decoy strategy [2]. However, in this earlier attempt, the clinical trial found no reduction in mortality. The ACE2 drug candidate, which is soluble and degrades in the body, also proved ineffective in neutralizing the virus.
Rather than give up on the idea, the UIC team decided to give it a try. They engineered a new soluble version of ACE2 that structurally might work better as a decoy than the original one. Their version of ACE2, which includes three changes in the protein’s amino acid building blocks, binds the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein much more tightly. In the lab, it also appeared to neutralize the virus as well as monoclonal antibodies used to treat COVID-19.
To put it to the test, they conducted studies in mice. Normal mice don’t get sick from SARS-CoV-2 because the viral spike can’t bind well to the mouse version of the ACE2 receptor. So, the researchers did their studies in a mouse that carries the human ACE2 and develops a severe acute respiratory syndrome somewhat similar to that seen in humans with severe COVID-19.
In their studies, using both the original viral isolate from Washington State and the Gamma variant (P.1) first detected in Brazil, they found that infected mice infused with their therapeutic ACE2 protein had much lower mortality and showed few signs of severe acute respiratory syndrome. While the protein worked against both versions of the virus, infection with the more aggressive Gamma variant required earlier treatment. The treated mice also regained their appetite and weight, suggesting that they were making a recovery.
Further studies showed that the decoy bound to spike proteins from every variant tested, including Alpha, Beta, Delta and Epsilon. (Omicron wasn’t yet available at the time of the study.) In fact, the decoy bound just as well, if not better, to new variants compared to the original virus.
The researchers will continue their preclinical work. If all goes well, they hope to move their ACE2 decoy into a clinical trial. What’s especially promising about this approach is it could be used in combination with treatments that work in other ways, such as by preventing virus that’s already infected cells from growing or limiting an excessive and damaging immune response to the infection.
Last week, more than 17,500 people in the United States were hospitalized with severe COVID-19. We’ve got to continue to do all we can to save lives, and it will take lots of innovative ideas, like this ACE2 decoy, to put us in a better position to beat this virus once and for all.
References:
[1] Engineered ACE2 decoy mitigates lung injury and death induced by SARS-CoV-2 variants.
Zhang L, Dutta S, Xiong S, Chan M, Chan KK, Fan TM, Bailey KL, Lindeblad M, Cooper LM, Rong L, Gugliuzza AF, Shukla D, Procko E, Rehman J, Malik AB. Nat Chem Biol. 2022 Jan 19.
[2] Recombinant human angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (rhACE2) as a treatment for patients with COVID-19 (APN01-COVID-19). ClinicalTrials.gov.
Links:
COVID-19 Research (NIH)
Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (NIH)
Asrar Malik (University of Illinois Chicago)
Jalees Rehman (University of Illinois Chicago)
NIH Support: National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute; National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases
Single-Cell Study Offers New Clue into Causes of Cystic Fibrosis
Posted on by Dr. Francis Collins

More than 30 years ago, I co-led the Michigan-Toronto team that discovered that cystic fibrosis (CF) is caused by an inherited misspelling in the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) gene [1]. The CFTR protein’s normal function on the surface of epithelial cells is to serve as a gated channel for chloride ions to pass in and out of the cell. But this function is lost in individuals for whom both copies of CFTR are misspelled. As a consequence, water and salt get out of balance, leading to the production of the thick mucus that leaves people with CF prone to life-threatening lung infections.
It took three decades, but that CFTR gene discovery has now led to the development of a precise triple drug therapy that activates the dysfunctional CFTR protein and provides major benefit to most children and adults with CF. But about 10 percent of individuals with CF have mutations that result in the production of virtually no CFTR protein, which means there is nothing for current triple therapy to correct or activate.
That’s why more basic research is needed to tease out other factors that contribute to CF and, if treatable, could help even more people control the condition and live longer lives with less chronic illness. A recent NIH-supported study, published in the journal Nature Medicine [2], offers an interesting basic clue, and it’s visible in the image above.
The healthy lung tissue (left) shows a well-defined and orderly layer of ciliated cells (green), which use hair-like extensions to clear away mucus and debris. Running closely alongside it is a layer of basal cells (outlined in red), which includes stem cells that are essential for repairing and regenerating upper airway tissue. (DNA indicating the position of cell is stained in blue).
In the CF-affected airways (right), those same cell types are present. However, compared to the healthy lung tissue, they appear to be in a state of disarray. Upon closer inspection, there’s something else that’s unusual if you look carefully: large numbers of a third, transitional cell subtype (outlined in red with green in the nucleus) that combines properties of both basal stem cells and ciliated cells, which is suggestive of cells in transition. The image below more clearly shows these cells (yellow arrows).

The increased number of cells with transitional characteristics suggests an unsuccessful attempt by the lungs to produce more cells capable of clearing the mucus buildup that occurs in airways of people with CF. The data offer an important foundation and reference for continued study.
These findings come from a team led by Kathrin Plath and Brigitte Gomperts, University of California, Los Angeles; John Mahoney, Cystic Fibrosis Foundation, Lexington, MA; and Barry Stripp, Cedars-Sinai, Los Angeles. Together with their lab members, they’re part of a larger research team assembled through the Cystic Fibrosis Foundation’s Epithelial Stem Cell Consortium, which seeks to learn how the disease changes the lung’s cellular makeup and use that new knowledge to make treatment advances.
In this study, researchers analyzed the lungs of 19 people with CF and another 19 individuals with no evidence of lung disease. Those with CF had donated their lungs for research in the process of receiving a lung transplant. Those with healthy lungs were organ donors who died of other causes.
The researchers analyzed, one by one, many thousands of cells from the airway and classified them into subtypes based on their distinctive RNA patterns. Those patterns indicate which genes are switched on or off in each cell, as well as the degree to which they are activated. Using a sophisticated computer-based approach to sift through and compare data, the team created a comprehensive catalog of cell types and subtypes present in healthy airways and in those affected by CF.
The new catalogs also revealed that the airways of people with CF had alterations in the types and proportions of basal cells. Those differences included a relative overabundance of cells that appeared to be transitioning from basal stem cells into the specialized ciliated cells, which are so essential for clearing mucus from the lungs.
We are not yet at our journey’s end when it comes to realizing the full dream of defeating CF. For the 10 percent of CF patients who don’t benefit from the triple-drug therapy, the continuing work to find other treatment strategies should be encouraging news. Keep daring to dream of breathing free. Through continued research, we can make the story of CF into history!
References:
[1] Identification of the cystic fibrosis gene: chromosome walking and jumping. Rommens JM, Iannuzzi MC, Kerem B, Drumm ML, Melmer G, Dean M, Rozmahel R, Cole JL, Kennedy D, Hidaka N, et al. Science.1989 Sep 8;245(4922):1059-65.
[2] Transcriptional analysis of cystic fibrosis airways at single-cell resolution reveals altered epithelial cell states and composition. Carraro G, Langerman J, Sabri S, Lorenzana Z, Purkayastha A, Zhang G, Konda B, Aros CJ, Calvert BA, Szymaniak A, Wilson E, Mulligan M, Bhatt P, Lu J, Vijayaraj P, Yao C, Shia DW, Lund AJ, Israely E, Rickabaugh TM, Ernst J, Mense M, Randell SH, Vladar EK, Ryan AL, Plath K, Mahoney JE, Stripp BR, Gomperts BN. Nat Med. 2021 May;27(5):806-814.
Links:
Cystic Fibrosis (National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute/NIH)
Kathrin Plath (University of California, Los Angeles)
Brigitte Gomperts (UCLA)
Stripp Lab (Cedars-Sinai, Los Angeles)
Cystic Fibrosis Foundation (Lexington, MA)
Epithelial Stem Cell Consortium (Cystic Fibrosis Foundation, Lexington, MA)
NIH Support: National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute; National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases; National Institute of General Medical Sciences; National Cancer Institute; National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences
How Severe COVID-19 Can Tragically Lead to Lung Failure and Death
Posted on by Dr. Francis Collins
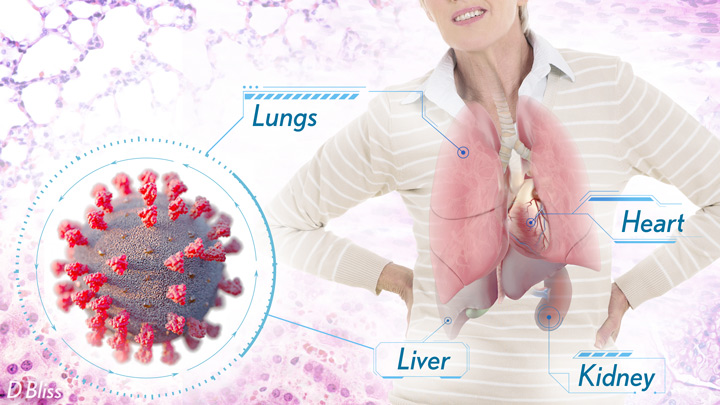
More than 3 million people around the world, now tragically including thousands every day in India, have lost their lives to severe COVID-19. Though incredible progress has been made in a little more than a year to develop effective vaccines, diagnostic tests, and treatments, there’s still much we don’t know about what precisely happens in the lungs and other parts of the body that leads to lethal outcomes.
Two recent studies in the journal Nature provide some of the most-detailed analyses yet about the effects on the human body of SARS-CoV-2, the coronavirus that causes COVID-19 [1,2]. The research shows that in people with advanced infections, SARS-CoV-2 often unleashes a devastating series of host events in the lungs prior to death. These events include runaway inflammation and rampant tissue destruction that the lungs cannot repair.
Both studies were supported by NIH. One comes from a team led by Benjamin Izar, Columbia University, New York. The other involves a group led by Aviv Regev, now at Genentech, and formerly at Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard, Cambridge, MA.
Each team analyzed samples of essential tissues gathered from COVID-19 patients shortly after their deaths. Izar’s team set up a rapid autopsy program to collect and freeze samples within hours of death. He and his team performed single-cell RNA sequencing on about 116,000 cells from the lung tissue of 19 men and women. Similarly, Regev’s team developed an autopsy biobank that included 420 total samples from 11 organ systems, which were used to generate multiple single-cell atlases of tissues from the lung, kidney, liver, and heart.
Izar’s team found that the lungs of people who died of COVID-19 were filled with immune cells called macrophages. While macrophages normally help to fight an infectious virus, they seemed in this case to produce a vicious cycle of severe inflammation that further damaged lung tissue. The researchers also discovered that the macrophages produced high levels of IL-1β, a type of small inflammatory protein called a cytokine. This suggests that drugs to reduce effects of IL-1β might have promise to control lung inflammation in the sickest patients.
As a person clears and recovers from a typical respiratory infection, such as the flu, the lung repairs the damage. But in severe COVID-19, both studies suggest this isn’t always possible. Not only does SARS-CoV-2 destroy cells within air sacs, called alveoli, that are essential for the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide, but the unchecked inflammation apparently also impairs remaining cells from repairing the damage. In fact, the lungs’ regenerative cells are suspended in a kind of reparative limbo, unable to complete the last steps needed to replace healthy alveolar tissue.
In both studies, the lung tissue also contained an unusually large number of fibroblast cells. Izar’s team went a step further to show increased numbers of a specific type of pathological fibroblast, which likely drives the rapid lung scarring (pulmonary fibrosis) seen in severe COVID-19. The findings point to specific fibroblast proteins that may serve as drug targets to block deleterious effects.
Regev’s team also describes how the virus affects other parts of the body. One surprising discovery was there was scant evidence of direct SARS-CoV-2 infection in the liver, kidney, or heart tissue of the deceased. Yet, a closer look heart tissue revealed widespread damage, documenting that many different coronary cell types had altered their genetic programs. It’s still to be determined if that’s because the virus had already been cleared from the heart prior to death. Alternatively, the heart damage might not be caused directly by SARS-CoV-2, and may arise from secondary immune and/or metabolic disruptions.
Together, these two studies provide clearer pictures of the pathology in the most severe and lethal cases of COVID-19. The data from these cell atlases has been made freely available for other researchers around the world to explore and analyze. The hope is that these vast data sets, together with future analyses and studies of people who’ve tragically lost their lives to this pandemic, will improve our understanding of long-term complications in patients who’ve survived. They also will now serve as an important foundational resource for the development of promising therapies, with the goal of preventing future complications and deaths due to COVID-19.
References:
[1] A molecular single-cell lung atlas of lethal COVID-19. Melms JC, Biermann J, Huang H, Wang Y, Nair A, Tagore S, Katsyv I, Rendeiro AF, Amin AD, Schapiro D, Frangieh CJ, Luoma AM, Filliol A, Fang Y, Ravichandran H, Clausi MG, Alba GA, Rogava M, Chen SW, Ho P, Montoro DT, Kornberg AE, Han AS, Bakhoum MF, Anandasabapathy N, Suárez-Fariñas M, Bakhoum SF, Bram Y, Borczuk A, Guo XV, Lefkowitch JH, Marboe C, Lagana SM, Del Portillo A, Zorn E, Markowitz GS, Schwabe RF, Schwartz RE, Elemento O, Saqi A, Hibshoosh H, Que J, Izar B. Nature. 2021 Apr 29.
[2] COVID-19 tissue atlases reveal SARS-CoV-2 pathology and cellular targets. Delorey TM, Ziegler CGK, Heimberg G, Normand R, Shalek AK, Villani AC, Rozenblatt-Rosen O, Regev A. et al. Nature. 2021 Apr 29.
Links:
COVID-19 Research (NIH)
Izar Lab (Columbia University, New York)
Aviv Regev (Genentech, South San Francisco, CA)
NIH Support: National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences; National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute; National Cancer Institute; National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases; National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases; National Human Genome Research Institute; National Institute of Mental Health; National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism
Mapping Severe COVID-19 in the Lungs at Single-Cell Resolution
Posted on by Dr. Francis Collins

A crucial question for COVID-19 researchers is what causes progression of the initial infection, leading to life-threatening respiratory illness. A good place to look for clues is in the lungs of those COVID-19 patients who’ve tragically lost their lives to acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), in which fluid and cellular infiltrates build up in the lung’s air sacs, called alveoli, keeping them from exchanging oxygen with the bloodstream.
As shown above, a team of NIH-funded researchers has done just that, capturing changes in the lungs over the course of a COVID-19 infection at unprecedented, single-cell resolution. These imaging data add evidence that SARS-CoV-2, the coronavirus that causes COVID-19, primarily infects cells at the surface of the air sacs. Their findings also offer valuable clues for treating the most severe consequences of COVID-19, suggesting that a certain type of scavenging immune cell might be driving the widespread lung inflammation that leads to ARDS.
The findings, published in Nature [1], come from Olivier Elemento and Robert E. Schwartz, Weill Cornell Medicine, New York. They already knew from earlier COVID-19 studies about the body’s own immune response causing the lung inflammation that leads to ARDS. What was missing was an understanding of the precise interplay between immune cells and lung tissue infected with SARS-CoV-2. It also wasn’t clear how the ARDS seen with COVID-19 compared to the ARDS seen in other serious respiratory diseases, including influenza and bacterial pneumonia.
Traditional tissue analysis uses chemical stains or tagged antibodies to label certain proteins and visualize important features in autopsied human tissues. But using these older techniques, it isn’t possible to capture more than a few such proteins at once. To get a more finely detailed view, the researchers used a more advanced technology called imaging mass cytometry [2].
This approach uses a collection of lanthanide metal-tagged antibodies to label simultaneously dozens of molecular markers on cells within tissues. Next, a special laser scans the labeled tissue sections, which vaporizes the heavy metal tags. As the metals are vaporized, their distinct signatures are detected in a mass spectrometer along with their spatial position relative to the laser. The technique makes it possible to map precisely where a diversity of distinct cell types is located in a tissue sample with respect to one another.
In the new study, the researchers applied the method to 19 lung tissue samples from patients who had died of severe COVID-19, acute bacterial pneumonia, or bacterial or influenza-related ARDS. They included 36 markers to differentiate various types of lung and immune cells as well as the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein and molecular signs of immune activation, inflammation, and cell death. For comparison, they also mapped four lung tissue samples from people who had died without lung disease.
Altogether, they captured more than 200 lung tissue maps, representing more than 660,000 cells across all the tissues sampled. Those images showed in all cases that respiratory infection led to a thickening of the walls surrounding alveoli as immune cells entered. They also showed an increase in cell death in infected compared to healthy lungs.
Their maps suggest that what happens in the lungs of COVID-19 patients who die with ARDS isn’t entirely unique. It’s similar to what happens in the lungs of those with other life-threatening respiratory infections who also die with ARDS.
They did, however, reveal a potentially prominent role in COVID-19 for white blood cells called macrophages. The results showed that macrophages are much more abundant in the lungs of severe COVID-19 patients compared to other lung infections.
In late COVID-19, macrophages also increase in the walls of alveoli, where they interact with lung cells known as fibroblasts. This suggests these interactions may play a role in the buildup of damaging fibrous tissue, or scarring, in the alveoli that tends to be seen in severe COVID-19 respiratory infections.
While the virus initiates this life-threatening damage, its progression may not depend on the persistence of the virus, but on an overreaction of the immune system. This may explain why immunomodulatory treatments like dexamethasone can provide benefit to the sickest patients with COVID-19. To learn even more, the researchers are making their data and maps available as a resource for scientists around the world who are busily working to understand this devastating illness and help put an end to the terrible toll caused by this pandemic.
References:
[1] The spatial landscape of lung pathology during COVID-19 progression. Rendeiro AF, Ravichandran H, Bram Y, Chandar V, Kim J, Meydan C, Park J, Foox J, Hether T, Warren S, Kim Y, Reeves J, Salvatore S, Mason CE, Swanson EC, Borczuk AC, Elemento O, Schwartz RE. Nature. 2021 Mar 29.
[2] Mass cytometry imaging for the study of human diseases-applications and data analysis strategies. Baharlou H, Canete NP, Cunningham AL, Harman AN, Patrick E. Front Immunol. 2019 Nov 14;10:2657.
Links:
COVID-19 Research (NIH)
Elemento Lab (Weill Cornell Medicine, New York)
Schwartz Lab (Weill Cornell Medicine)
NIH Support: National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences; National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases; National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases; National Cancer Institute
Trying to Make Sense of Long COVID Syndrome
Posted on by Dr. Francis Collins

More than 400,000 Americans have now lost their lives to COVID-19. But thousands of others who’ve gotten sick and survived COVID-19 are finding that a full recovery can be surprisingly elusive. Weeks and months after seemingly recovering from even mild cases of COVID-19, many battle a wide range of health problems.
Indeed, new results from the largest global study of this emerging “Long COVID syndrome” highlight just how real and pressing this public health concern really is. The study, reported recently as a pre-print on medRxiv, is based on survey results from more than 3,700 self-described COVID “Long Haulers” in 56 countries [1]. They show nearly half couldn’t work full time six months after unexpectedly developing prolonged symptoms of COVID-19. A small percentage of respondents, thankfully, seemed to have bounced back from brief bouts of Long COVID, though time will tell whether they have fully recovered.
These findings are the second installment from the online Body Politic COVID-19 Support Group and its Patient-Led Research for COVID-19, which consists of citizen scientists with a wide range of expertise in the arts and sciences who are struggling with the prolonged effects of COVID-19 themselves. In an earlier survey, this group provided a first-draft description of Long COVID syndrome, based on the self-reported experiences of 640 respondents.
In the new survey-based study led by Athena Akrami, with Patient-Led Research for COVID-19 and University College London, England, the goal was to characterize the experiences of many more people with Long COVID syndrome. They now define the syndrome as a collection of symptoms lasting for more than 28 days.
This second survey emphasizes the course and severity of more than 200 symptoms over time, including those affecting the heart, lungs, gastrointestinal system, muscles, and joints. It took a particularly in-depth look at neurological and neuropsychiatric symptoms, along with the ability of COVID-19 survivors to return to work and participate in other aspects of everyday life.
The 3,762 individuals who responded to the survey were predominately white females, between the ages of 30 and 60, who lived in the United States. As in the previous survey, the study included adults with symptoms consistent with COVID-19, whether or not the infection had been confirmed by a viral or antibody test. That is a potential weakness of the study, as some of these individuals may have had some other inciting illness. But many of the study’s participants developed symptoms early on in the pandemic, when testing was much more limited than it is now.
More than half never sought hospital care. Only 8 percent said that they’d been admitted to the hospital for COVID-19. And yet, 2,464 respondents reported COVID-19 symptoms lasting six months or longer. Most of the remaining respondents also continued to have symptoms, although they had not yet reached the six-month mark.
Among the most common symptoms were fatigue, worsening of symptoms after physical or mental activity, shortness of breath, trouble sleeping, and “brain fog,” or difficulty thinking clearly. The majority—88 percent—said they coped with some form of cognitive dysfunction or memory loss that to varying degrees affected their everyday lives. That includes the ability to make decisions, have conversations, follow instructions, and drive.
Those who had prolonged symptoms of COVID-19 for more than six months reported contending with about 14 symptoms on average. Most also reported that they’d had a relapse of symptoms, seemingly triggered by exercise, mental activity, or just everyday stress. When surveyed, nearly half of respondents said they’d had to reduce their hours at work due to the severity of their symptoms. Another 22 percent weren’t working at all due to their Long COVID.
The findings show that—even in those people who don’t require hospitalization for severe COVID-19—the condition’s prolonged symptoms are having a major impact on lives and livelihoods, both here and around the world. While the number of people affected isn’t yet known, if even a small proportion of the vast numbers of people infected with COVID-19 develop Long COVID syndrome, it represents a significant public health concern.
Another recent study from China further documents the tendency of COVID-19-related symptoms to linger past the usual recovery time for a respiratory virus [2]. The study, published in Lancet, showed that six months after the onset of illness, more than 75 percent of people hospitalized with COVID-19 in Wuhan between January and May 2020 continued to report at least one symptom. Fatigue, muscle weakness, sleep difficulties, anxiety, and depression all were common. More than half of individuals also had significant persistent lung abnormalities, which were more common in those who’d been more severely ill.
It’s essential for us to learn all we can about how SARS-CoV-2, which is the coronavirus that causes COVID-19, leads to such widespread symptoms. It’s also essential that we develop ways to better treat or prevent these symptoms. The NIH held a workshop last month to summarize what is known and fill in key gaps in our knowledge about Long COVID syndrome, which is clinically known as post-acute sequelae of COVID-19 (PASC). In December, Congress authorized funding for continued research on PASC, including an appropriation of funds for NIH to support continued study of these prolonged health consequences.
As these efforts and others proceed in the coming months, the hope is that we’ll gain much more insight and get some answers soon. And, if you’ve had or are currently experiencing symptoms of COVID-19, there’s still time to share your data by participating in the Patient-Led Research for COVID-19’s second survey.
References:
[1] Characterizing Long COVID in an international cohort: 7 months of symptoms and their impact. David HE et al. Medrxiv. 27 December 27 2020.
[2] 6-month consequences of COVID-19 in patients discharged from hospital: a cohort study. Huang C, Huang L, et al. Lancet. 2021 Jan 16;397(10270):220-232.
Links:
COVID-19 Research (NIH)
Akrami Lab (Sainsbury Wellcome Center, University College London, England)
Patient-led Research for COVID-19
Video: Workshop on Post-Acute Sequelae of COVID-19 (NIH)
Mini-Lungs in a Lab Dish Mimic Early COVID-19 Infection
Posted on by Dr. Francis Collins

Researchers have become skilled at growing an array of miniature human organs in the lab. Such lab-grown “organoids” have been put to work to better understand diabetes, fatty liver disease, color vision, and much more. Now, NIH-funded researchers have applied this remarkable lab tool to produce mini-lungs to study SARS-CoV-2, the coronavirus that causes COVID-19.
The intriguing bubble-like structures (red/clear) in the mini-lung pictured above represent developing alveoli, the tiny air sacs in our lungs, where COVID-19 infections often begin. In this organoid, the air sacs consist of many thousands of cells, all of which arose from a single adult stem cell isolated from tissues found deep within healthy human lungs. When carefully nurtured in lab dishes, those so-called alveolar epithelial type-2 cells (AT2s) begin to multiply. As they grow, they spontaneously assemble into structures that closely resemble alveoli.
A team led by Purushothama Rao Tata, Duke University School of Medicine, Durham, NC, developed these mini-lungs in a quest to understand how adult stem cells help to regenerate damaged tissue in the deepest recesses of the lungs, where SARS-CoV-2 attacks. In earlier studies, the researchers had shown it was possible for these cells to produce miniature alveoli. But there was a problem: the “soup” they used to nurture the growing cells included ingredients that weren’t well defined, making it hard to characterize the experiments fully.
In the study, now reported in Cell Stem Cell, the researchers found a way to simplify and define that brew. For the first time, they could produce mini-lungs consisting only of human lung cells. By growing them in large numbers in the lab, they can now learn more about SARS-CoV-2 infection and look for new ways to prevent or treat it.
Tata and his collaborators at the University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill, have already confirmed that SARS-CoV-2 infects the mini-lungs via the critical ACE2 receptor, just as the virus is known to do in the lungs of an infected person.
Interestingly, the cells also produce cytokines, inflammatory molecules that have been tied to tissue damage. The findings suggest the cytokine signals may come from the lungs themselves, even before immune cells arrive on the scene.
The heavily infected lung cells eventually self-destruct and die. In an unexpected turn of events, they even induce cell death in some neighboring healthy cells that are not infected. The relevance of the studies to the clinic was boosted by the finding that the gene activity patterns in the mini-lungs are a close match to those found in samples taken from six patients with severe COVID-19.
Now that he’s got the recipe down, Tata is busy making organoids and helping to model COVID-19 infections, with the hope of identifying and testing promising new treatments. It’s clear these mini-lungs are breathing some added life into the basic study of COVID-19.
Reference:
[1] Human lung stem cell-based alveolospheres provide insights into SARS-CoV-2-mediated interferon responses and pneumocyte dysfunction. Katsura H, Sontake V, Tata A, Kobayashi Y, Edwards CE, Heaton BE, Konkimalla A, Asakura T, Mikami Y, Fritch EJ, Lee PJ, Heaton NS, Boucher RC, Randell SH, Baric RS, Tata PR. Cell Stem Cell. 2020 Oct 21:S1934-5909(20)30499-9.
Links:
Coronavirus (COVID-19) (NIH)
Tata Lab (Duke University School of Medicine, Durham, NC)
NIH Support: National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases; National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute; National Institute of General Medical Sciences; National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases
Next Page