deep mutational scanning
How Immunity Generated from COVID-19 Vaccines Differs from an Infection
Posted on by Dr. Francis Collins
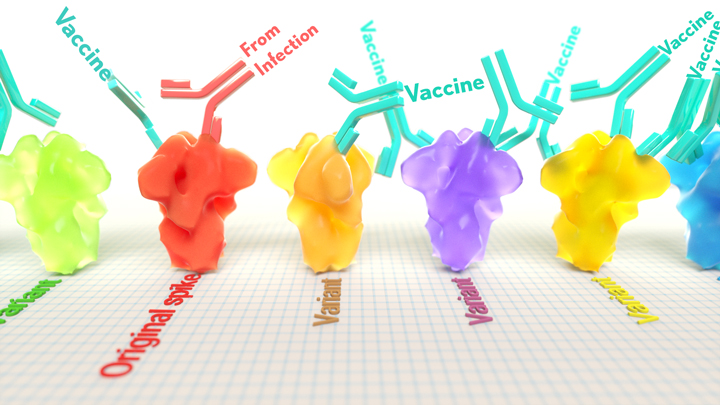
A key issue as we move closer to ending the pandemic is determining more precisely how long people exposed to SARS-CoV-2, the COVID-19 virus, will make neutralizing antibodies against this dangerous coronavirus. Finding the answer is also potentially complicated with new SARS-CoV-2 “variants of concern” appearing around the world that could find ways to evade acquired immunity, increasing the chances of new outbreaks.
Now, a new NIH-supported study shows that the answer to this question will vary based on how an individual’s antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 were generated: over the course of a naturally acquired infection or from a COVID-19 vaccine. The new evidence shows that protective antibodies generated in response to an mRNA vaccine will target a broader range of SARS-CoV-2 variants carrying “single letter” changes in a key portion of their spike protein compared to antibodies acquired from an infection.
These results add to evidence that people with acquired immunity may have differing levels of protection to emerging SARS-CoV-2 variants. More importantly, the data provide further documentation that those who’ve had and recovered from a COVID-19 infection still stand to benefit from getting vaccinated.
These latest findings come from Jesse Bloom, Allison Greaney, and their team at Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center, Seattle. In an earlier study, this same team focused on the receptor binding domain (RBD), a key region of the spike protein that studs SARS-CoV-2’s outer surface. This RBD is especially important because the virus uses this part of its spike protein to anchor to another protein called ACE2 on human cells before infecting them. That makes RBD a prime target for both naturally acquired antibodies and those generated by vaccines. Using a method called deep mutational scanning, the Seattle group’s previous study mapped out all possible mutations in the RBD that would change the ability of the virus to bind ACE2 and/or for RBD-directed antibodies to strike their targets.
In their new study, published in the journal Science Translational Medicine, Bloom, Greaney, and colleagues looked again to the thousands of possible RBD variants to understand how antibodies might be expected to hit their targets there [1]. This time, they wanted to explore any differences between RBD-directed antibodies based on how they were acquired.
Again, they turned to deep mutational scanning. First, they created libraries of all 3,800 possible RBD single amino acid mutants and exposed the libraries to samples taken from vaccinated individuals and unvaccinated individuals who’d been previously infected. All vaccinated individuals had received two doses of the Moderna mRNA vaccine. This vaccine works by prompting a person’s cells to produce the spike protein, thereby launching an immune response and the production of antibodies.
By closely examining the results, the researchers uncovered important differences between acquired immunity in people who’d been vaccinated and unvaccinated people who’d been previously infected with SARS-CoV-2. Specifically, antibodies elicited by the mRNA vaccine were more focused to the RBD compared to antibodies elicited by an infection, which more often targeted other portions of the spike protein. Importantly, the vaccine-elicited antibodies targeted a broader range of places on the RBD than those elicited by natural infection.
These findings suggest that natural immunity and vaccine-generated immunity to SARS-CoV-2 will differ in how they recognize new viral variants. What’s more, antibodies acquired with the help of a vaccine may be more likely to target new SARS-CoV-2 variants potently, even when the variants carry new mutations in the RBD.
It’s not entirely clear why these differences in vaccine- and infection-elicited antibody responses exist. In both cases, RBD-directed antibodies are acquired from the immune system’s recognition and response to viral spike proteins. The Seattle team suggests these differences may arise because the vaccine presents the viral protein in slightly different conformations.
Also, it’s possible that mRNA delivery may change the way antigens are presented to the immune system, leading to differences in the antibodies that get produced. A third difference is that natural infection only exposes the body to the virus in the respiratory tract (unless the illness is very severe), while the vaccine is delivered to muscle, where the immune system may have an even better chance of seeing it and responding vigorously.
Whatever the underlying reasons turn out to be, it’s important to consider that humans are routinely infected and re-infected with other common coronaviruses, which are responsible for the common cold. It’s not at all unusual to catch a cold from seasonal coronaviruses year after year. That’s at least in part because those viruses tend to evolve to escape acquired immunity, much as SARS-CoV-2 is now in the process of doing.
The good news so far is that, unlike the situation for the common cold, we have now developed multiple COVID-19 vaccines. The evidence continues to suggest that acquired immunity from vaccines still offers substantial protection against the new variants now circulating around the globe.
The hope is that acquired immunity from the vaccines will indeed produce long-lasting protection against SARS-CoV-2 and bring an end to the pandemic. These new findings point encouragingly in that direction. They also serve as an important reminder to roll up your sleeve for the vaccine if you haven’t already done so, whether or not you’ve had COVID-19. Our best hope of winning this contest with the virus is to get as many people immunized now as possible. That will save lives, and reduce the likelihood of even more variants appearing that might evade protection from the current vaccines.
Reference:
[1] Antibodies elicited by mRNA-1273 vaccination bind more broadly to the receptor binding domain than do those from SARS-CoV-2 infection. Greaney AJ, Loes AN, Gentles LE, Crawford KHD, Starr TN, Malone KD, Chu HY, Bloom JD. Sci Transl Med. 2021 Jun 8.
Links:
COVID-19 Research (NIH)
Bloom Lab (Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center, Seattle)
NIH Support: National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases
Mapping Which Coronavirus Variants Will Resist Antibody Treatments
Posted on by Dr. Francis Collins

You may have heard about the new variants of SARS-CoV-2—the coronavirus that causes COVID-19—that have appeared in other parts of the world and have now been detected in the United States. These variants, particularly one called B.1.351 that was first identified in South Africa, have raised growing concerns about the extent to which their mutations might help them evade current antibody treatments and highly effective vaccines.
While researchers take a closer look, it’s already possible in the laboratory to predict which mutations will help SARS-CoV-2 evade our therapies and vaccines, and even to prepare for the emergence of new mutations before they occur. In fact, an NIH-funded study, which originally appeared as a bioRxiv pre-print in November and was recently peer-reviewed and published in Science, has done exactly that. In the study, researchers mapped all possible mutations that would allow SARS-CoV-2 to resist treatment with three different monoclonal antibodies developed for treatment of COVID-19 [1].
The work, led by Jesse Bloom, Allison Greaney, and Tyler Starr, Fred Hutchinson Cancer Center, Seattle, focused on the receptor binding domain (RBD), a key region of the spike protein that studs SARS-CoV-2’s outer surface. The virus uses RBD to anchor itself to the ACE2 receptor of human cells before infecting them. That makes the RBD a prime target for the antibodies that our bodies generate to defend against the virus.
In the new study, researchers used a method called deep mutational scanning to find out which mutations positively or negatively influence the RBD from being able to bind to ACE2 and/or thwart antibodies from striking their target. Here’s how it works: Rather than waiting for new mutations to arise, the researchers created a library of RBD fragments, each of which contained a change in a single nucleotide “letter” that would alter the spike protein’s shape and/or function by swapping one amino acid for another. It turns out that there are more than 3,800 such possible mutations, and Bloom’s team managed to make all but a handful of those versions of the RBD fragment.
The team then used a standard laboratory approach to measure systematically how each of those single-letter typos altered RBD’s ability to bind ACE2 and infect human cells. They also measured how those changes affected three different therapeutic antibodies from recognizing and binding to the viral RBD. Those antibodies include two developed by Regeneron (REGN10933 and REGN10987), which have been granted emergency use authorization for treatment of COVID-19 together as a cocktail called REGN-COV2. They also looked at an antibody developed by Eli Lilly (LY-CoV016), which is now in phase 3 clinical trials for treating COVID-19.
Based on the data, the researchers created four mutational maps for SARS-CoV-2 to escape each of the three therapeutic antibodies, as well as for the REGN-COV2 cocktail. Their studies show most of the mutations that would allow SARS-CoV-2 to escape treatment differed between the two Regeneron antibodies. That’s encouraging because it indicates that the virus likely needs more than one mutation to become resistant to the REGN-COV2 cocktail. However, it appears there’s one spot where a single mutation could allow the virus to resist REGN-COV2 treatment.
The escape map for LY-CoV016 similarly showed a number of mutations that could allow the virus to escape. Importantly, while some of those changes might impair the virus’s ability to cause infection, most of them appeared to come at little to no cost to the virus to reproduce.
How do these laboratory data relate to the real world? To begin to explore this question, the researchers teamed up with Jonathan Li, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston. They looked at an immunocompromised patient who’d had COVID-19 for an unusually long time and who was treated with the Regeneron cocktail for 145 days, giving the virus time to replicate and acquire new mutations.
Viral genome data from the infected patient showed that these maps can indeed be used to predict likely paths of viral evolution. Over the course of the antibody treatment, SARS-CoV-2 showed changes in the frequency of five mutations that would change the makeup of the spike protein and its RBD. Based on the newly drawn escape maps, three of those five are expected to reduce the efficacy of REGN10933. One of the others is expected to limit binding by the other antibody, REGN10987.
The researchers also looked to data from all known circulating SARS-CoV-2 variants as of Jan. 11, 2021, for evidence of escape mutations. They found that a substantial number of mutations with potential to allow escape from antibody treatment already are present, particularly in parts of Europe and South Africa.
However, it’s important to note that these maps reflect just three important antibody treatments. Bloom says they’ll continue to produce maps for other promising therapeutic antibodies. They’ll also continue to explore where changes in the virus could allow for escape from the more diverse set of antibodies produced by our immune system after a COVID-19 infection or vaccination.
While it’s possible some COVID-19 vaccines may offer less protection against some of these new variants—and recent results have suggested the AstraZeneca vaccine may not provide much protection against the South African variant, there’s still enough protection in most other current vaccines to prevent serious illness, hospitalization, and death. And the best way to keep SARS-CoV-2 from finding new ways to escape our ongoing efforts to end this terrible pandemic is to double down on whatever we can do to prevent the virus from multiplying and spreading in the first place.
For now, emergence of these new variants should encourage all of us to take steps to slow the spread of SARS-CoV-2. That means following the three W’s: Wear a mask, Watch your distance, Wash your hands often. It also means rolling up our sleeves to get vaccinated as soon as the opportunity arises.
Reference:
[1] Prospective mapping of viral mutations that escape antibodies used to treat COVID-19.
Starr TN, Greaney AJ, Addetia A, Hannon WW, Choudhary MC, Dingens AS, Li JZ, Bloom JD.
Science. 2021 Jan 25:eabf9302.
Links:
COVID-19 Research (NIH)
Bloom Lab (Fred Hutchinson Cancer Center, Seattle)
NIH Support: National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases
Deciphering Another Secret of Life
Posted on by Dr. Francis Collins

In 1953, Francis Crick famously told the surprised customers at the Eagle and Child pub in London that he and Jim Watson had discovered the secret of life. When NIH’s Marshall Nirenberg and his colleagues cracked the genetic code in 1961, it was called the solution to life’s greatest secret. Similarly, when the complete human genome sequence was revealed for the first time in 2003, commentators (including me) referred to this as the moment where the book of life for humans was revealed. But there are many more secrets of life that still need to be unlocked, including figuring out the biochemical rules of a protein shape-shifting phenomenon called allostery [1].
Among those taking on this ambitious challenge is a recipient of a 2018 NIH Director’s New Innovator Award, Srivatsan Raman of the University of Wisconsin-Madison. If successful, such efforts could revolutionize biology by helping us better understand how allosteric proteins reconfigure themselves in the right shapes at the right times to regulate cell signaling, metabolism, and many other important biological processes.
What exactly is an allosteric protein? Proteins have active, or orthosteric, sites that turn the proteins off or on when specific molecules bind to them. Some proteins also have less obvious regulatory, or allosteric, sites that indirectly affect the proteins’ activity when outside molecules bind to them. In many instances, allosteric binding triggers a change in the shape of the protein.
Allosteric proteins include oxygen-carrying hemoglobin and a variety of enzymes crucial to human health and development. In his work, Raman will start by studying a relatively simple bacterial protein, consisting of less than 200 amino acids, to understand the basics of how allostery works over time and space.
Raman, who is a synthetic biologist, got the idea for this project a few years ago while tinkering in the lab to modify an allosteric protein to bind new molecules. As part of the process, he and his team used a new technology called deep mutational scanning to study the functional consequences of removing individual amino acids from the protein [2].
The screen took them on a wild ride of unexpected functional changes, and a new research opportunity called out to him. He could combine this scanning technology with artificial intelligence and other cutting-edge imaging and computational tools to probe allosteric proteins more systematically in hopes of deciphering the basic molecular rules of allostery.
With the New Innovator Award, Raman’s group will first create a vast number of protein mutants to learn how best to determine the allosteric signaling pathway(s) within a protein. They want to dissect out the properties of each amino acid and determine which connect into a binding site and precisely how those linkages are formed. The researchers also want to know how the amino acids tend to configure into an inactive state and how that structure changes into an active state.
Based on these initial studies, the researchers will take the next step and use their dataset to predict where allosteric pathways are found in individual proteins. They will also try to figure out if allosteric signals are sent in one direction only or whether they can be bidirectional.
The experiments will be challenging, but Raman is confident that they will serve to build a more unified view of how allostery works. In fact, he hopes the data generated—and there will be a massive amount—will reveal novel sites to control or exploit allosteric signaling. Such information will not only expand fundamental biological understanding, but will accelerate efforts to discover new therapies for diseases, such as cancer, in which disruption of allosteric proteins plays a crucial role.
References:
[1] Allostery: an illustrated definition for the ‘second secret of life.’ Fenton AW. Trends Biochem Sci. 2008 Sep;33(9):420-425.
[2] Engineering an allosteric transcription factor to respond to new ligands. Taylor ND, Garruss AS, Moretti R, Chan S, Arbing MA, Cascio D, Rogers JK, Isaacs FJ, Kosuri S, Baker D, Fields S, Church GM, Raman S. Nat Methods. 2016 Feb;13(2):177-183.
Links:
Drug hunters explore allostery’s advantages. Jarvis LM, Chemical & Engineering News. 2019 March 10
Allostery: An Overview of Its History, Concepts, Methods, and Applications. Liu J, Nussinov R. PLoS Comput Biol. 2016 Jun 2;12(6):e1004966.
Srivatsan Raman (University of Wisconsin-Madison)
Raman Project Information (NIH RePORTER)
NIH Director’s New Innovator Award (Common Fund/NIH)
NIH Support: National Institute of General Medical Sciences; Common Fund
