skin disorder
Eczema Relief: Probiotic Lotion Shows Early Promise
Posted on by Dr. Francis Collins
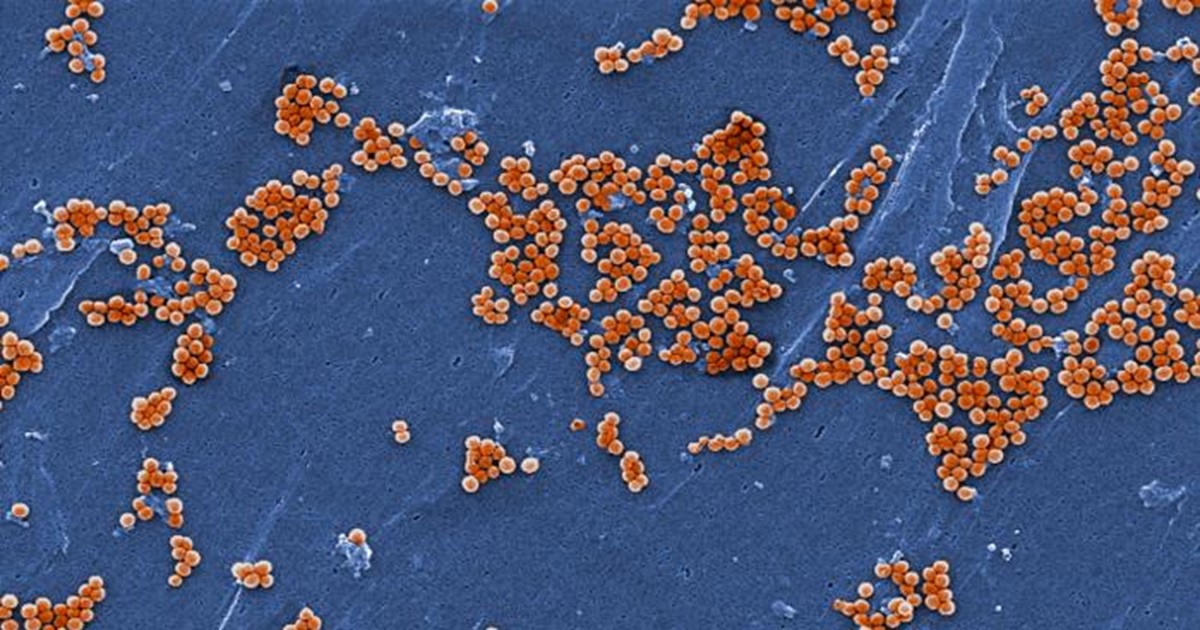
Caption: Scanning electron microscopic image of Staphylococcus aureus bacteria (orange).
Credit: CDC/Jeff Hageman, MHS
Over the years, people suffering from eczema have slathered their skin with lotions containing everything from avocado oil to zinc oxide. So, what about a lotion that features bacteria as the active ingredient? That might seem like the last thing a person with a skin problem would want to do, but it’s actually a very real possibility, based on new findings that build upon the growing realization that many microbes living in and on the human body—our microbiome—are essential for good health. The idea behind such a bacterial lotion is that good bugs can displace bad bugs.
Eczema is a noncontagious inflammatory skin condition characterized by a dry, itchy rash. It most commonly affects the cheeks, arms, and legs. Previous studies have suggested that the balance of microbes present on people with eczema is different than on those with healthy skin [1]. One major difference is a proliferation of a bad type of bacteria, called Staphylococcus aureus.
Recently, an NIH-funded research team found that healthy human skin harbors beneficial strains of Staphylococcus bacteria with the power to keep Staph aureus in check. To see if there might be a way to restore this natural balance artificially, the researchers created a lotion containing the protective bacteria and tested it on the arms of volunteers who had eczema [2]. Just 24 hours after one dose of the lotion was applied, the researchers found the volunteers’ skin had greatly reduced levels of Staph aureus. While further study is needed to learn whether the treatment can improve skin health, the findings suggest that similar lotions might offer a new approach for treating eczema and other skin conditions. Think of it as a probiotic for the skin!
